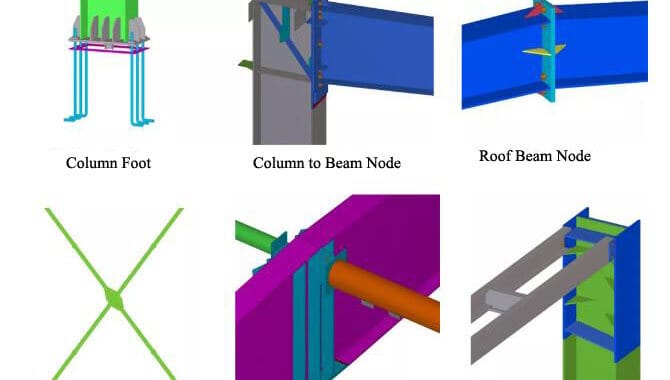
Steel structure splicing includes splicing in the workshop and on-site. The splicing methods include welding and bolting. We should implement…
Steel structures are widely used in various construction projects due to their many advantages, such as being lightweight, easy to install, short construction periods, good seismic performance, and low environmental pollution. Steel building components are usually prefabricated and can be assembled directly on the construction site, which not only improves construction efficiency but also significantly shortens the construction period and reduces on-site construction’s complexity and environmental impact.
Introduction of steel building components
The main frame of the steel structure building consists of roof beams and steel columns. These key components together constitute the skeleton of the building and determine the overall type, size and bearing capacity of the steel structure building. The main steel frame bears essential functions, not only supporting the load of the roof and walls but also withstanding the influence of external natural factors, such as strong winds, rainfall, snowstorms, and even earthquakes, to ensure the stability and safety of the building.
I-beam steel frame
In the steel structure system, I-beam steel frame is the most common structural form. Steel columns and roof beams can be hot-rolled or welded I-beams with high bearing capacity and good bending resistance.
Steel columns and beams are usually designed in two forms: equilateral and tapered structures. When designing, it is necessary to accurately calculate and optimize the design according to the width of the building, the load it bears, and other relevant requirements. For example, in large industrial workshops or warehouses, larger cross-section steel beams and columns may be selected to accommodate larger load requirements.
Single-span structure
A single-span structure refers to a portal frame supported by a beam at both ends, with only two support points in the horizontal direction. The distance between the support points is called the “span”. A significant advantage of the single-span structure is that there are no internal support columns, which can provide a wide column-free space, suitable for buildings that require large open spaces.
The width of the single-span steel frame can be designed using tapered or straight columns, and the span can be extended to 60 meters to meet large space requirements. Single-span structures are widely used in places such as churches, office buildings, garages, hangars, gymnasiums, etc., especially for buildings that require open spaces or barrier-free spaces.

Multi-span structure
A multi-span structure is similar to a single-span portal frame structure, the only difference is that it has more than two support points in the horizontal direction. Multi-span steel structure buildings are supported by the combined action of beams and columns, using multiple support points to effectively share the load and enhance the stability of the overall structure. Since support columns are added internally to increase strength, the activity space and usable area of steel structure buildings are expanded. Multi-span structures are often used in large industrial plants, storage facilities, shopping malls, stadiums, and other buildings that require higher strength and larger space.

Steel building components: Primary Structure
1. Foundation
The foundation is a load-bearing component where the steel building components are in contact with the ground. Its main function is to transfer the load of the upper structure to the foundation or soil evenly and stably to ensure the stability of the building. The foundation must be strong, stable and reliable.
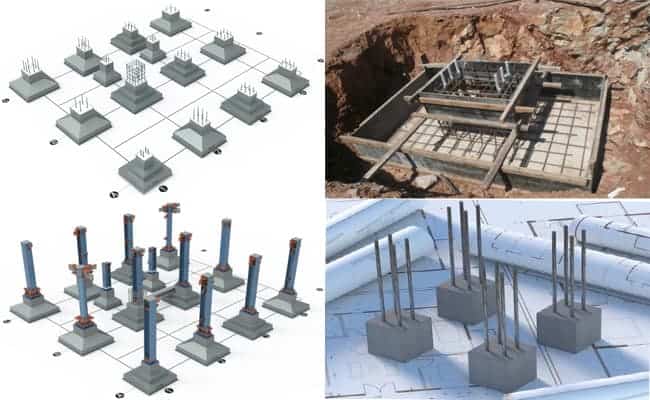
2. Embedded parts
Generally, when doing civil engineering or foundation, in order to facilitate the installation of structures on the foundation or facilitate future equipment, some equipment bases, anchor bolts, auxiliary steel plate structures, etc. are placed on the foundation first. After the foundation is completed, subsequent equipment can be easily fixed on the embedded plate or components. This is very common in engineering.
3. Column
The column is a component in the steel structure that bears the main vertical load. The function of the column is to support the upper beams, trusses, floor slabs and other structures, and transfer the load to the foundation. According to the cross-sectional form, the column can be divided into square columns, round columns, tubular columns, rectangular columns, I-beam columns, H-shaped columns, cross-shaped columns, lattice columns, etc. Columns of different forms are designed according to the load, span and functional requirements of the building.

Columns play a critical role in structures, and their local damage may cause the collapse or instability of the entire structure. For example, independent columns bear the load of the upper structure of the building, while gable wind-resistant columns mainly play a role in wind resistance, while enhancing the earthquake resistance and stability of the building. The design of columns should not only consider the load-bearing capacity, but also the stability of the building. Especially in high-rise buildings and large industrial facilities, the design and layout of columns are particularly important.
4. Beams
Beams are transverse members that mainly bear lateral forces, bending moments and shear forces from the upper structure. The deformation mode of beams is mainly bending, and their main function is to transfer loads and support the upper structure. The design of beams usually works together with columns and other vertical members to form the spatial structural system of the entire building.
According to the cross-sectional form, beams can be divided into rectangular cross-sectional beams, T-shaped cross-sectional beams, I-shaped cross-sectional beams, special-shaped cross-sectional beams, etc. According to their functions and locations, beams can be divided into structural beams (such as foundation beams, steel beams, etc.), ring beams, lintels, tension beams, etc. The function of beams is not only support, but also plays a structural role such as crack resistance, earthquake resistance and stability. Different types of beams are designed according to their location and load requirements to ensure the safety and stability of the building structure.
5. Crane beams
Crane beams are specially used to carry crane equipment. They are commonly found in buildings such as industrial plants and warehouses that require cranes. Crane beams are generally installed on the upper part of the plant, and the crane travels back and forth on the crane beams through tracks to transport heavy objects. The design of crane beams needs to take into account the working load of the crane, the dynamic load of the crane, and the span requirements of the plant, so crane beams usually have greater strength and stiffness.
The design of crane beams must not only meet the load requirements, but also ensure the smooth operation and safety of the crane. When designing, special attention should be paid to the connection method between the crane beam and the supporting structure and the running track of the crane to ensure the stability and service life of the crane.
6. Trusses
A truss is a plane or space structure composed of straight rods. The main feature of the truss structure is that it can effectively withstand axial tension or pressure, thereby making full use of the strength of the material. Trusses are widely used in buildings with large spans or high heights. Trusses are an ideal choice, especially when it is necessary to save materials, reduce deadweight, and increase rigidity.
Compared with traditional solid beams, truss structures can significantly reduce deadweight and increase overall rigidity, so they are particularly suitable for large-span buildings, bridges, and roof structures. Truss structures can not only provide sufficient bearing capacity, but also effectively save materials and reduce construction costs.
Steel building components: Secondary Structure
The secondary structures assist the primary structure and play a stabilizing role.
Secondary structures include horizontal roof bracing, wall bracing, tie beam, roof purlins, wall girt, and secondary structures made of cold-formed steel, such as round steel, angle steel, round pipe, C-shaped or Z-shaped steel.
1. Tie-beam
It is the strut that the steel column and the steel column are connected horizontally. It is welded with steel pipes. It is used to resist the longitudinal force at the top of the column.
The tie beam is used to transmit axial force (such as wind load or crane longitudinal braking force), combined with cross horizontal bracing and cross wall bracing to form a stable longitudinal bracing system and increase the lateral stability of the beam and column members.
2. Roof horizontal bracing and wall bracing:
The roof load transferred from the roof bracing to the wall bracing and moved to the foundation. They are used to stabilize the primary steel frame.
3. Purlin, wall girt:
It comprises cold-formed C-shaped or Z-shaped steel. It is perpendicular to steel columns and roof beams. It is used to fix roof panels and wall panels. It also stabilizes the primary steel frame.
Working primarily with secondary steel frame systems, it provides all the strength needed for the metal structure building to meet the code and its intended use. Under pressure, steel can bend instead of breaking.
4. Sag rod:
A sag rod is used to Improve purlin stability.
The sag rods are generally made of round steel, and the diameter should not exceed 10mm. The setting of the braces is related to the span of the purlins. When the purlins span is 4m~6m, it is advisable to set the braces at the mid-span between the purlins. When the span is more excellent than 6m, the braces should be placed at one-third of the span of the purlins.
5. Flange bracing
The flange bracing is the support rod at the corner of the wall, between beams and columns, beams and purlins, and between columns and purlins. Those on the wall are called wall flange bracing, and those on the roof are called roof flange bracing.
Accessories for steel building components
Fasteners: Fasteners play the role of fastening connections in steel structure systems. Fasteners are mainly screws and bolts, including drill screws, anchor bolts, ordinary bolts, etc.;
Insulation materials: As an essential component of steel structure components, thermal insulation materials maximize their function of keeping out wind and rain. Insulation wool, rock wool boards, and sandwich panels are all thermal insulation materials.
Waterproof material: Waterproof material is the most technical accessory among steel structure accessories. It appears in accessories such as waterproof roll felt, coating, and butyl tape. Waterproof materials are the decisive factor for steel structure buildings to stand for twenty years.
Ventilation system: The ventilation system of steel structure buildings includes ridge ventilation and unpowered turbine ventilators.
Drainage system: Drainage pipes and gutters are responsible for drainage.
Windows and doors: Including aluminum alloy windows, rolling shutters, sliding doors, home doors, ventilators, and others.