The service life of steel structure buildings is more than 50 years. The roof and wall panels of prefabricated steel…
The light steel structure workshop is a new type of structure developed based on the standard steel structure, which includes all steel structures used under a light roof.
Compared with common steel structures, it has better economic indicators. The steel structure has not only lightweight, save the amount of steel, and has a fast construction speed, but also has strong seismic resistance, and can improve the overall seismic performance of the entire house. It is a structure widely used in industrial plants at present.
The light steel structure workshop consists of foundation beams, columns, purlins, roof, and walls.
The characteristics of light steel structure workshop:
- The use of the light roof not only reduces the section size of the beam and column but also reduces the foundation accordingly.
- The large gable roof with a ridge design in a multi-span building. Setting the internal columns can reduce the span of the beam, thereby reducing the cost.
- The lateral stiffness of the frame is guaranteed by purlin and fly bracing, eliminating longitudinal rigid members and reducing the width of the beam.
- The rigid steel frame can adopt the variable cross-section, and the cross-section is proportional to the bending moment; when changing the cross-section, the height and thickness of the beam can change as needed to achieve the best use of the material.
- The webs plate of the steel frame can design according to the effective width, which means that some web plates are allowed to lose its stability, and their post-buckling strength can use.
- The vertical load is usually the designed control load, but when the wind load is large or the workshop is high, the role of the wind load should not be ignored. In light roof gable frames, the earthquake action generally does not control it.
- The bracing can make lighter. Connect it to the web plate of the beam directly or with a horizontal joint plate, and it can use the round steel bar.
- All structural components manufactured in the factory, with a high degree of industrialization. The component units can be divided according to the transportation conditions, and the units are connected with bolts on-site, which is convenient and fast to install, and the amount of civil construction is small.
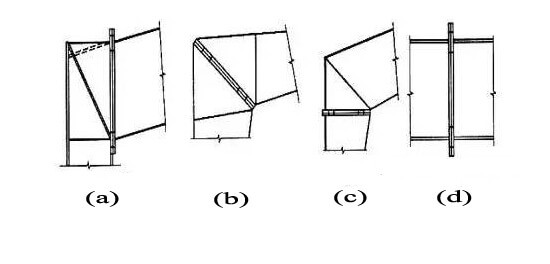
Steel beam and column connection and steel beam splicing:
For the connection of the beam and the column, the endplate can place vertically (figure a), the endplate obliquely (figure b), and the endplate horizontally (figure c). When splicing beams, the endplates should perpendicular to the outer edges of the components(figure d).
Purlin of Light Steel Structure Workshop:
- Channel purlin
Divided into ordinary channel steel purlins and light channel steel purlins. Ordinary channel steel purlin (figure a); due to the profile material is thick, the strength cannot fully exert, and the amount of steel used is large. Although light channel purlins improved over ordinary channel purlins, they are still not ideal. - Light H-shaped steel purlin
Light H-shaped steel purlin (figure b) with thin web and good bending stiffness, The inertia moments of the two main axes are relatively close, and the flange plate is straight and easy to connect. - C section steel
C section steel purlins: C section steel purlins (figure c) have large interchangeability, which widely used, saves steel, and easy to manufacture and install. - Z section steel
Z section steel purlin (figure d). Its main plane has high rigidity on the x-axis, small deflection when used as purlin, less steel consumption, and easy manufacturing and installation.
The connection structure of purlin
Purlins and roofs should reliably connect to ensure that roofs can prevent lateral instability and torsion of purlins, which is especially important for purlins that generally do not need to be checked for overall stability.
Self-tapping screws with rubber washers should use for the connection between purlin and corrugated single color roof sheets.
Tie beam and sag rod of purlin: bolted to each other.
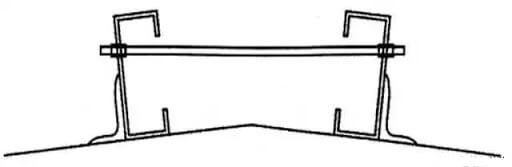
Purlin on the roof ridge:
The double-purlin scheme should be adopted for solid-belly purlins. Roof purlins can be connected with channel steel, angle steel, or round steel (see the figure below). When the truss purlin adopts the single purlin scheme at the ridge, although the amount of steel is less, the purlin models increase and the structure is complicated, it is generally appropriate to use the double purlin.