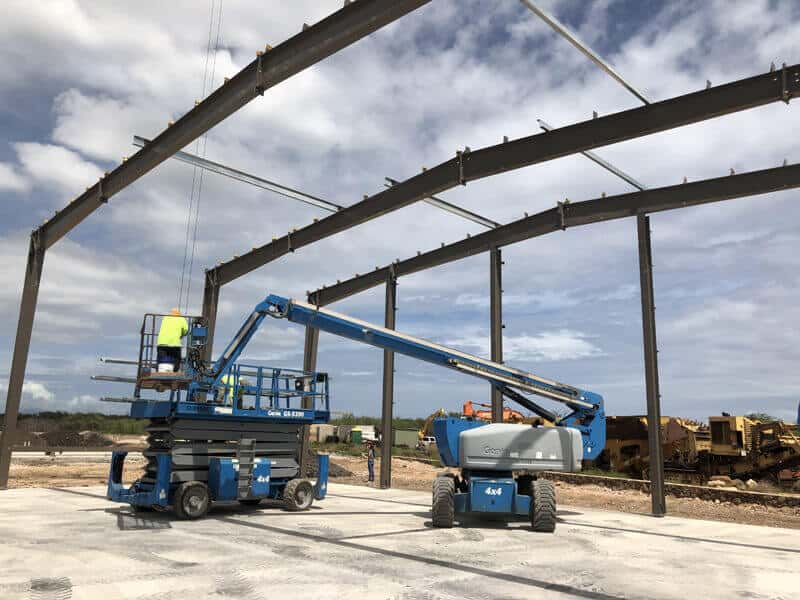
In the construction of modern storage facilities, steel structure warehouses have become one of the mainstream building forms due to…
Steel structure roof trusses refer to a single-row structure that bears roof loads. Steel columns and steel roof trusses form transverse steel trusses to support and carry the roof structure of the building. The primary function of the steel roof truss is to bear the weight of the building and external loads, such as wind, snow, etc.
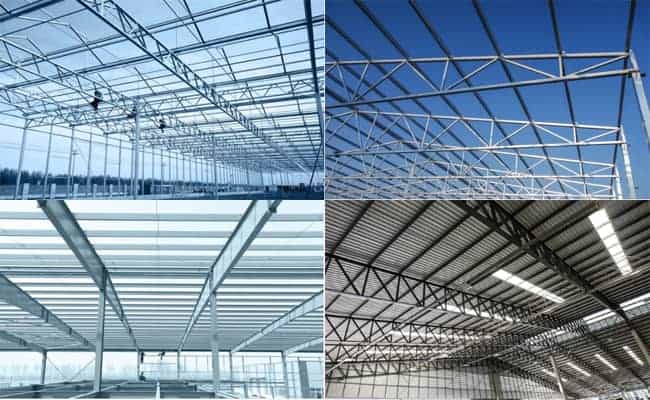

Classification of steel structure roof trusses:
Steel structure roof trusses are divided into three categories according to their shapes: triangular roof trusses, trapezoidal roof trusses, and parallel chord roof trusses. Roof truss rods are divided into upper, web, and lower chord rods. The abdominal pole is split into a straight pole and a diagonal brace.
According to the weight of the roof truss, a single roof truss weighing less than one ton is generally called a light steel roof truss. Typically, the profile section of a light steel roof truss is smaller.
1. Triangular roof truss
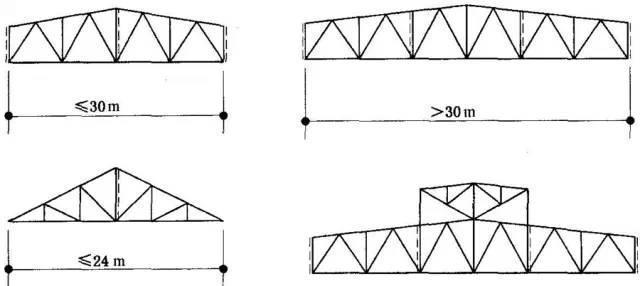
Triangular roof trusses are suitable for purlin roofs with steep slopes. They are hinged with columns and span less than or equal to 24m. Triangular roof trusses are divided into Fink roof trusses and herringbone roof trusses.
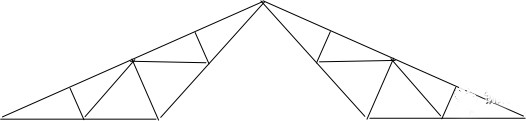
Fink roof trusses: uneven distribution of internal forces
Herringbone roof trusses: When there is a suspended ceiling, set the web rods at the dotted line
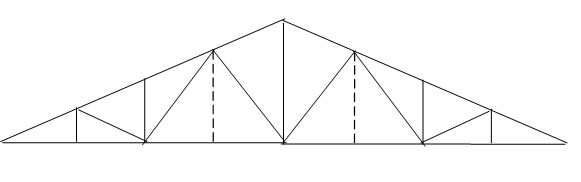
2. Trapezoidal roof truss
The trapezoidal roof truss is suitable for roofs with a gentle slope. The internal force of the chords is evenly distributed and can be hinged or rigidly connected to the columns.
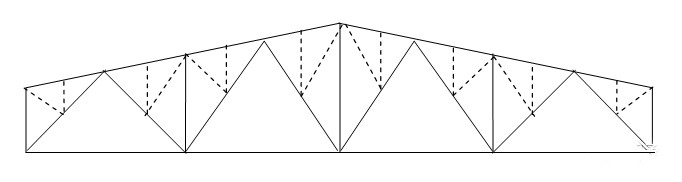
3. Parallel chord roof truss
The chord and web members are of equal length, the node form is the same, the members are standardized, and the node structure is uniform, but the internal force distribution of the chord member is uneven. They are mainly used for single-slope roofs, brackets, crane brake trusses, support components, etc.
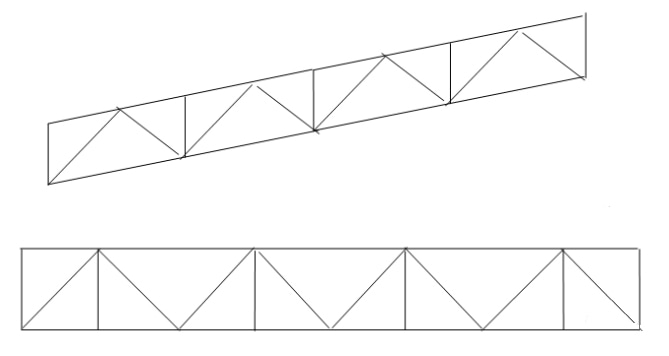
Vertical support
Vertical support function: A practical component makes two adjacent roof trusses form a spatially geometrically invariant system to ensure lateral stability.
Set location:
Set in a column space with upper chord transverse supports;
In the direction of the roof truss span, one or more channels should be set in the middle of the span according to the roof truss form and span size.
Trapezoidal roof truss:
When the span is ≤30 m:
Vertical support should be arranged in the plane of the vertical poles at the mid-span and both ends of the roof truss;
When the span is >30 m:
When there is no skylight, vertical support should be arranged at 1/3 of the roof truss span and in the plane of the vertical poles at both ends.
Vertical supports should be arranged on both sides of the skylight frame jambs when there is a skylight.
Triangular roof truss:
When the span is ≤24 m, vertical support should be set up in the plane of the span center pole;
When the span is >24 m, two vertical supports should be arranged according to the specific conditions;
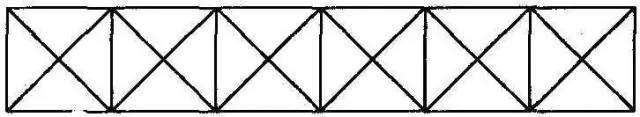
Roof supports are generally in the form of parallel chord trusses.
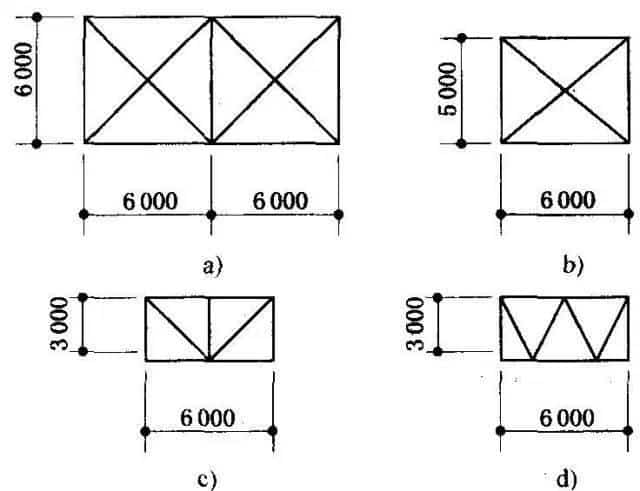
The web rods are in the form of crosses and are generally used for upper-chord transverse, lower-chord transverse, and lower-chord longitudinal horizontal supports (Figure a).
The intersections of the longitudinal horizontal support truss are preferably formed into a square shape, generally 6m×6m, or a rectangular shape, such as 6m×3m. The distance between transverse horizontal support nodes is 2 to 4 times the distance between the upper chord nodes of the roof truss.
The form of web rods for vertical supports can be determined according to the width-to-height ratio of the truss.
When the width and height are close, cross diagonal bars can be used (Figure b);
When the height is small, V-type and W-type inclined rods can be used (Figure c, d). The intersection angle between the chord rod and the inclined rod is 30°~60º.
Material of steel structure roof truss
The cross-section form of the steel structure roof truss rods is generally angle steel, and steel pipes or rectangular tubes are also used to make the roof trusses.
H-shaped steel roof truss
At present, general steel structure buildings rarely use triangular or trapezoidal roof trusses made of angle steel. Generally, H-shaped steel beams are made in sections, and then each H-shaped steel beam is connected to a herringbone-shaped double slope or multiple sections through high-strength bolts—slope steel roof trusses.
Processing, production, and installation of H-shaped steel roof trusses
H-shaped steel roof trusses are first processed and manufactured in the steel structure processing and manufacturing plant according to each section of H-shaped steel beams.
The processing and manufacturing process is similar to that of H-shaped steel columns. After being processed into finished products, they are transported to the construction site. Each section of steel beams is fixed with high-strength bolts.
After being connected on-site, the steel roof truss is formed and hoisted using a crane.
The installation process of H-shaped steel roof trusses is as follows:
(1) Assemble the segmented steel beams as a whole
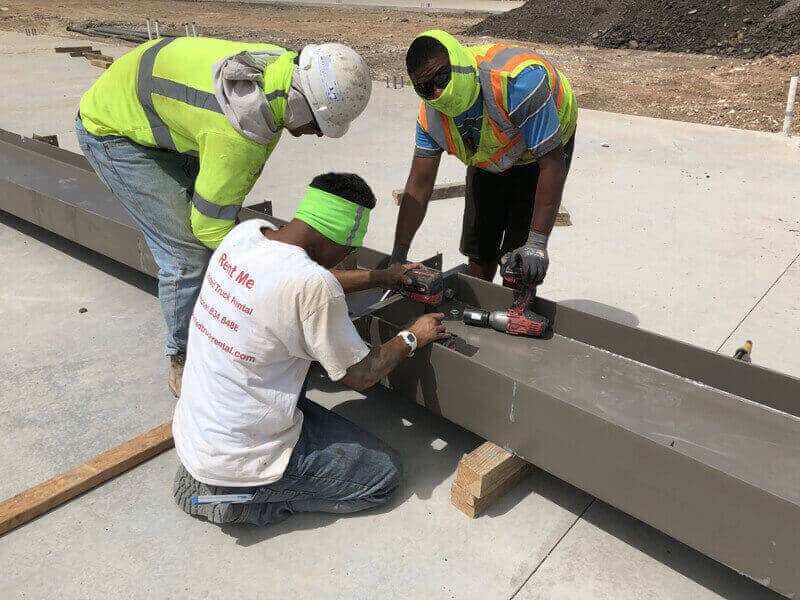

(2) As shown below, install a lifeline shelf on the steel beam before lifting and tightening the lifeline. Fasten both ends. Set up a shelf every 4-5 meters to ensure stability and make the lifeline as tight as possible.
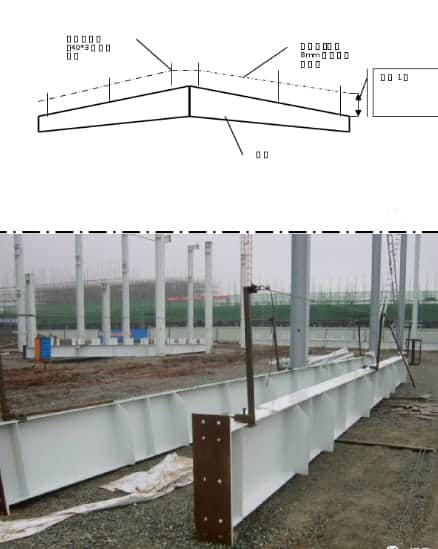
(3) As shown in the figure below, the installer should go up the ladder to a position close to the top of the column in advance (note that the safety belt should be hung into the screw holes of each connecting plate of the column first).
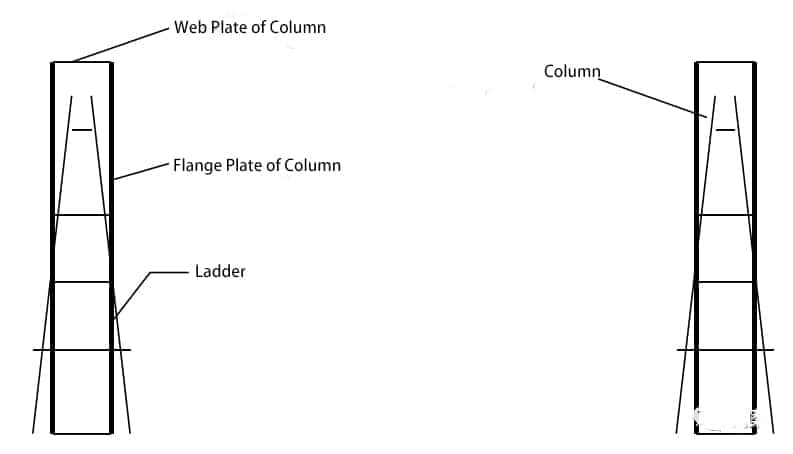
Each person should prepare a tool kit with related tools and a ladder. The lower end should be firmly padded and stabilized, and the upper end should be stuck into the column wing.
If the height of the bamboo ladder is >700mm from the top of the column, a crane with a cage should be used to lift personnel to the operating position.
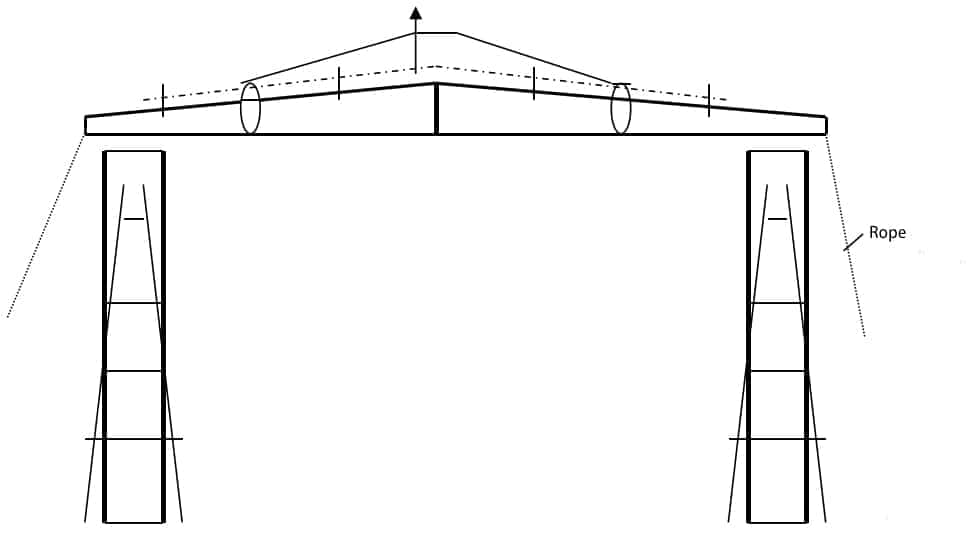
Ropes assist in the hoisting of steel beams to control the direction. After the steel beams hoisted are bolted and tightened, the operator can hang the safety belt on the lifeline and then walk on the steel beams.















