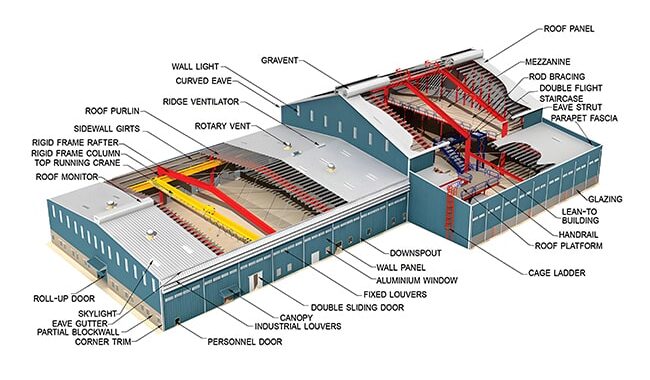
Steel structure splicing includes splicing in the workshop and on-site. The splicing methods include welding and bolting. We should implement…
What is a Steel Structure?
A steel structure is a load-bearing framework composed of interconnected steel components, including beams, columns, and braces. Designed to support heavy loads and resist external forces, it offers excellent strength, durability, and versatility across industrial, commercial, and infrastructure projects.

Common Structural Forms in Steel Construction
Steel structures come in various configurations, each tailored to different spatial, load-bearing, and architectural needs. Below are the most commonly used structural forms in modern construction.
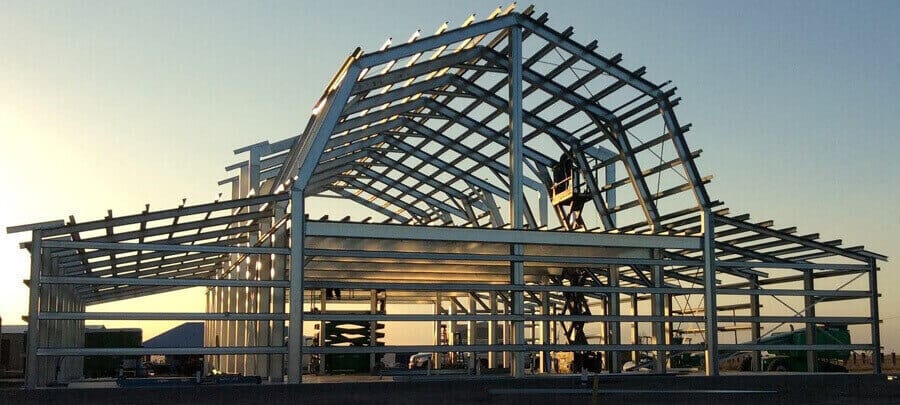
1. Portal Frame Structure
Portal frames consist of rigidly connected steel beams and columns that form a moment-resisting framework. This system is especially effective for low-rise industrial buildings where large, open floor areas are needed without interior supports—such as in warehouses, workshops, and aircraft hangars. The shape resembles a doorway, which is how the term “portal” originated.
Key Advantages:
- Simplified geometry allows for efficient load distribution under both vertical and lateral forces
- Faster and more cost-effective to build compared to conventional concrete framing
- Ideal for clear-span layouts with minimal interior obstructions
Typical Applications:
Industrial plants, storage buildings, agricultural facilities, and logistics warehouses.
FAQ – Is a portal frame structure suitable for earthquake-prone areas?
Yes. When designed with proper bracing, portal frames offer excellent seismic resistance due to their inherent rigidity and joint continuity.
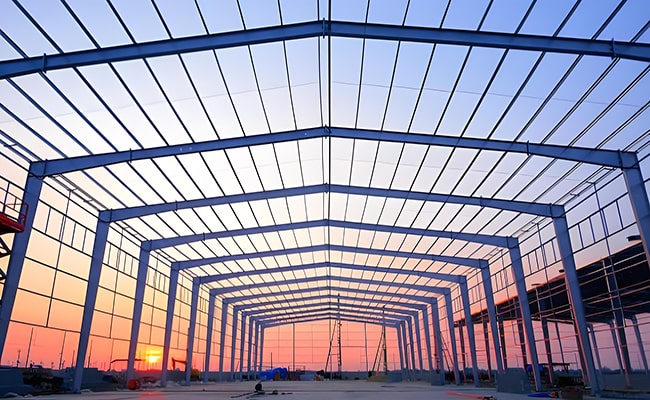

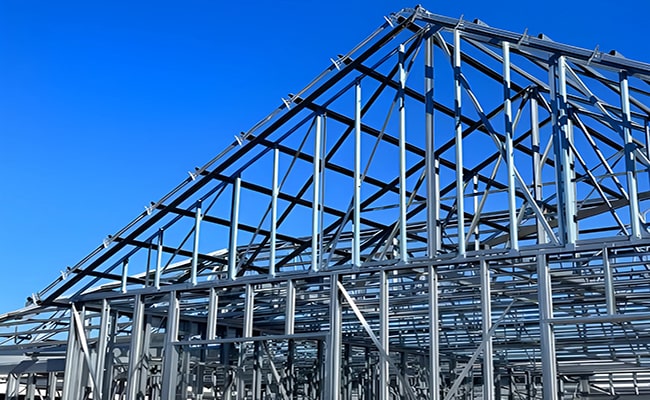
2. Multi-story Steel Frame Structure
This type of steel structure uses vertical steel columns and horizontal beams to form a skeletal framework that supports floors and walls. It allows for highly adaptable floor plans and can be scaled vertically, making it a preferred solution for complex urban buildings where space and functionality evolve over time.
Key Advantages:
- High redundancy ensures continued load distribution even if some elements fail.
- Excellent resistance to lateral loads from wind and earthquakes
- Facilitates flexible, open-plan interiors that can be reconfigured as needed
Typical Applications:
Commercial towers, hospitals, universities, hotels, and multi-unit residential complexes.
FAQ – Why Choose a Steel Frame Over Concrete for Tall Buildings?
Steel frames allow for lighter foundations, faster erection times, and more flexible interior layouts compared to traditional concrete systems.
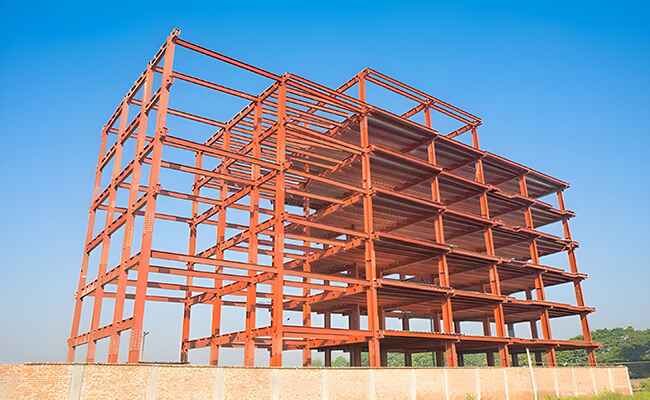

3. Steel Truss Structure
Trusses are triangulated steel assemblies made from slender members joined at nodes. Designed to carry loads primarily through axial tension and compression, they achieve long spans with remarkable efficiency and minimal material use. Their visual clarity also supports architectural expression.
Key Advantages:
- High stiffness-to-weight ratio enables very long spans
- Material-efficient solution for large open areas
- Performs exceptionally well under dynamic or repetitive loading
Typical Applications:
Bridges, airport hangars, sports arenas, and exhibition halls.
FAQ – What’s the main difference between a truss and a portal frame?
While both offer clear spans, trusses are lighter and better suited for very long spans; portal frames are simpler and often faster to erect.
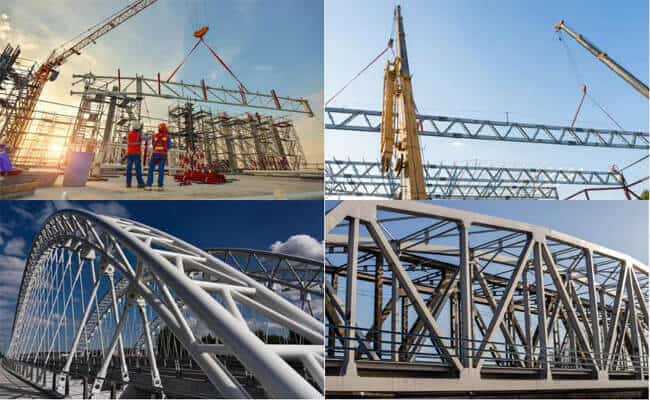

4. Space Frame Structure
A space frame is a three-dimensional structural system composed of interconnected struts arranged in a geometric grid. Unlike flat trusses, space frames carry loads in multiple directions, making them ideal for covering wide, open areas with minimal support.
Key Advantages:
- Uniform load transfer across all axes
- Modular units facilitate quick and precise factory fabrication
- Ideal for expansive roofs with minimal intermediate supports
Typical Applications:
Airport terminals, convention centers, large retail halls, and cultural venues with architectural openness.
FAQ – Are space frames structurally stronger than planar trusses?
In most cases, yes. Space frames distribute loads three-dimensionally, offering greater stability and stiffness with lower deflection over large spans.
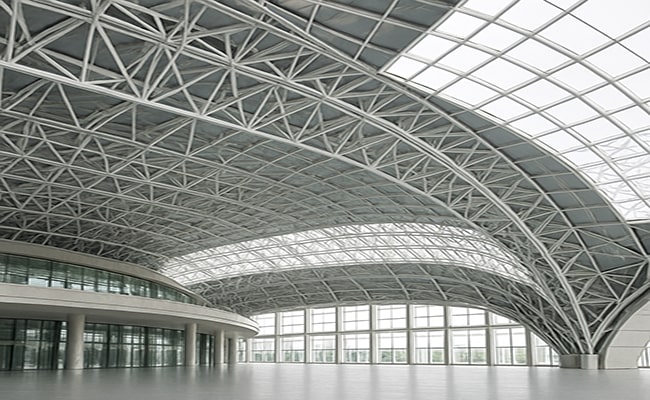

5. Light Steel Frame Structure
This steel structure system utilizes cold-formed, thin-gauge steel sections to create lightweight, yet strong and durable building frames. It’s especially effective in low-rise structures that benefit from fast construction and modular prefabrication.
Key Advantages:
- Lightweight for easier transport and faster assembly
- High-dimensional accuracy supports prefabrication and BIM integration
- Ideal for energy-efficient and thermally insulated building envelopes
Typical Applications:
Prefabricated housing, mobile offices, low-rise commercial units, and temporary structures.
FAQ: Is Light Steel Framing Better Than Wood Framing?
It depends. Steel is non-combustible, termite-resistant, and dimensionally stable—but typically has a higher material cost than wood.

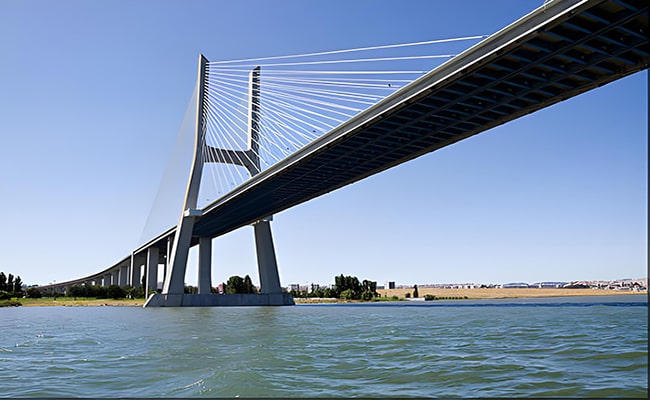
6. Cable-Stayed or Tension Structures
These structural systems utilize high-tensile steel cables, anchored to supports, to span large distances with minimal material mass. They are commonly used where both visual impact and engineering efficiency are required.
Key Advantages:
- Striking aesthetic appeal with minimal visual obstruction
- Enables ultra-long spans using very little structural depth
- Efficient use of materials for lightweight construction
Typical Applications:
Suspension bridges, tensile roofing systems, landmark pavilions, and stadium canopies.
FAQ – Are tension structures durable in harsh weather?
Yes, when properly engineered and maintained. The cables and membranes can be treated for UV, corrosion, and weather resistance to last for decades.

Strengths and Limitations of Steel Structures
Strengths
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Steel offers exceptional strength relative to its weight, enabling the design of slender, lightweight structures that can support substantial loads without excessive material use. This advantage is particularly valuable in long-span constructions like stadium roofs and airport terminals.
Rapid Construction
Thanks to prefabrication in controlled factory environments and efficient on-site assembly, steel structures can be erected in a fraction of the time required for traditional materials, significantly accelerating project schedules.
Design Flexibility
The malleability of steel accommodates complex architectural forms, intricate facades, and innovative spatial designs. From soaring skyscrapers to gracefully curved bridges, steel adapts to a wide range of aesthetic and functional demands.
Long-Term Durability
When protected against corrosion, steel structures demonstrate remarkable longevity, maintaining their strength and stability for decades even in challenging environments.
Sustainability
As one of the most recyclable construction materials, steel plays a crucial role in sustainable building practices, supporting the circular economy through repeated reuse without loss of performance.
Limitations
Corrosion Susceptibility
In aggressive environments such as coastal areas or chemical plants, steel requires specialized coatings or galvanization to prevent degradation over time.
Thermal Conductivity
Steel’s high thermal conductivity can lead to unwanted heat transfer, necessitating effective insulation strategies in energy-efficient designs to ensure occupant comfort and reduce operational costs.
Higher Initial Costs
While steel buildings often offer lower lifecycle costs, their initial investment—particularly in material procurement and precision fabrication—can be significantly higher than conventional alternatives like concrete or masonry.
Poor Acoustic Performance
Without supplemental insulation, steel frames can transmit sound more readily than heavier materials, potentially affecting acoustic comfort in sensitive spaces such as theaters, schools, and hospitals.
Key Performance Characteristics of Structural Steel
The performance of structural steel is influenced by its chemical composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing methods. Understanding these factors is essential for selecting the right material for specific engineering applications.
1. Influence of Chemical Composition
- Carbon and Manganese:
Increasing these elements enhances tensile and yield strength but may reduce ductility and weldability, requiring careful balance during material specification. - Sulfur and Phosphorus:
Excessive levels of these impurities can lead to brittleness, negatively impacting fatigue resistance and the reliability of welded joints. - Chromium and Nickel:
These alloying elements improve corrosion resistance and stability at elevated temperatures, making them essential for stainless and heat-resistant steels. - Copper:
The addition of copper increases resistance to atmospheric corrosion, particularly beneficial in marine and high-humidity environments.
2. Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength:
Critical for determining a structure’s capacity to resist pulling forces, assessed through standardized stress–strain testing. - Hardness:
A measure of surface resistance to indentation or scratching, evaluated using Brinell, Vickers, or Rockwell hardness tests. - Toughness:
Reflects a material’s ability to absorb energy during impact, directly related to fracture resistance under sudden loads. - Fatigue Strength:
Defines the endurance limit of steel under cyclic loading, crucial for structures subjected to repetitive stress like bridges and offshore platforms. - Corrosion Resistance:
Enhanced through alloying, galvanization, or protective coatings, ensuring the longevity of steel components in harsh environments.
3. Manufacturing and Forming
Unlike concrete, steel is not molded on-site. Structural steel elements are manufactured through hot or cold rolling processes in precision-controlled industrial mills, resulting in a wide array of standardized sections:
- Universal beams (H- and I-sections)
- Channels, angles, and tees
- Circular and rectangular hollow sections (tubular forms)
- Prefabricated trusses, girders, and specialized node assemblies
Prefabrication allows for consistent quality control, dimensional precision, and faster on-site integration, contributing to the overall efficiency of steel construction.
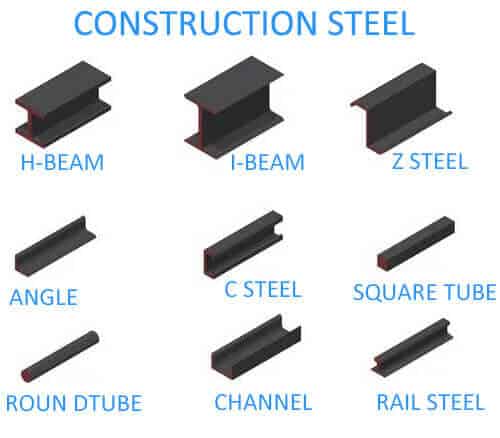
Read More: Structural Steel: 9 Types of Sections and Properties
International Standards for Steel Structures
To ensure structural reliability and global interoperability, various standard systems have been established:
GB 50017 (China): China’s national standard addressing design loads, detailing, durability, and safety criteria.
AISC (USA): The most widely recognized guideline in North America, covering load criteria, structural design, and connections.
BS 5950 (UK): Focuses on the balance of safety, economy, and structural efficiency.
EN 1993 – Eurocode 3 (EU): A harmonized framework for steel structure design across Europe.
Read more: steel structure design
End-to-End Construction Process of Steel Structures
Step 1: Planning & Feasibility
Project stakeholders collaboratively define functional requirements, site constraints, and preliminary budgets.
Step 2: Conceptual Design
Various structural schemes are proposed and evaluated for efficiency, feasibility, and architectural intent.
Step 3: Detailed Design
Engineers perform finite element analysis, specify connections and material grades, and prepare shop drawings.
Step 4: Procurement & Quality Control
Steel and auxiliary materials are sourced according to national and international standards with rigorous quality inspections.
Step 5: Fabrication
Components undergo cutting, welding, surface treatment, and assembly under CNC precision in factory settings.
Step 6: Logistics & Site Preparation
Components are organized by installation sequence and delivered to the site alongside foundational works.
Step 7: Erection & On-Site Assembly
Structures are erected using cranes and bolted/welded joints, ensuring dimensional accuracy and safety.
Step 8: Surface Protection
Coatings against fire and corrosion are applied, including intumescent paints and galvanized finishes.
Step 9: System Integration
Steel skeletons are integrated with other building systems (facades, MEP, roofing) through coordinated construction sequencing.
Step 10: Final Inspection & Handover
Completion checks include weld testing, structural verification, coating thickness inspection, and documentation for future maintenance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical lifespan of a steel structure?
With proper maintenance and design, steel structures can reliably serve for over 50 years.
How does steel perform in seismic zones?
Exceptionally well—its ductility and lightweight characteristics absorb and dissipate seismic energy efficiently.
Is steel structure construction environmentally friendly?
Yes. Steel’s recyclability and reduced construction waste align it with green building standards.
Can steel buildings be expanded later?
Absolutely. The modular nature of steel structures facilitates future modifications and functional upgrades.
Are steel structures suitable for housing?
Increasingly so. Prefabricated steel homes offer energy efficiency, fast construction, and architectural versatility.
How is corrosion prevented in steel structures?
Corrosion is mitigated through the use of protective coatings, galvanization, and weathering steel in environments prone to moisture and harsh conditions.