In the construction of modern storage facilities, steel structure warehouses have become one of the mainstream building forms due to…
A steel frame is a structure made of steel, usually connected by welding, bolting, or riveting steel beams, columns, bracing, and other components. It is generally used as the main load-bearing structure of a building. Steel frames have the advantages of being lightweight, high strength, good seismic performance, and fast construction speed and can meet the needs of large-span buildings and complex structures.
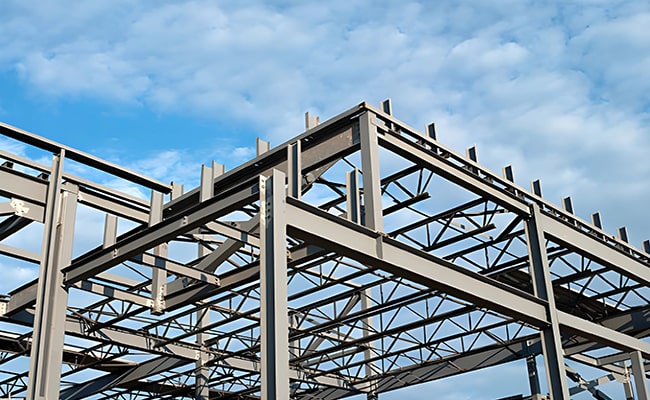

Introduction to steel frame structure
In modern buildings, steel structures occupy an essential position. As its core component, steel frames are widely used in various buildings and industrial fields. Steel frame construction includes four basic steps: design, processing, transportation, and installation. First, the structural engineer calculates the cross-section of the steel frame according to the load and external environment and then draws detailed drawings. Then, the factory cuts, welds, drills, and treats the steel according to the processing drawings. After processing, it is transported to the site for assembly, forming a steel frame structure.
The role of steel in modern buildings
Steel is an ideal building material. Its high strength and durability make it meaningful in modern buildings. Compared with traditional concrete, steel is light in weight but has a higher load-bearing capacity, reducing the foundation’s burden. In addition, steel buildings have a short construction period, and 90% of the materials can be recycled and reused. Although the initial investment is higher than that of concrete, in the long run, the economic benefits of steel structures are far more significant than those of concrete structures.
Typical applications of steel frames in different industries
Steel frame structures are used in many industries, including workshops, warehouses, bridges, gymnasiums, multi-storey shopping malls, and high-rise buildings. Steel frames can withstand heavy equipment in a workshop or the industrial field. In the field of infrastructure, steel frame structures can provide bridges with superior durability and earthquake resistance. Steel frames can provide large spans and flexible layouts in gymnasiums and commercial buildings. Steel frame structures can improve construction efficiency and service life in high-rise buildings.
Types of steel frame structures
1. Rigid frame structure: strength and stability
Rigid frame structure is one of the main structural types. It is lightweight, highly reliable, and has sound vibration (shock) resistance and impact resistance. Rigid frame structure is widely used in multi-story buildings. This structure consists of many beams and columns that bear the entire load of the house. For high-rise civil buildings and multi-storey industrial plants, brick walls can no longer meet the requirements of heavy loads, and frames are often used as load-bearing structures. Rigid frames have strong bearing capacity and remain stable under wind loads and earthquakes.
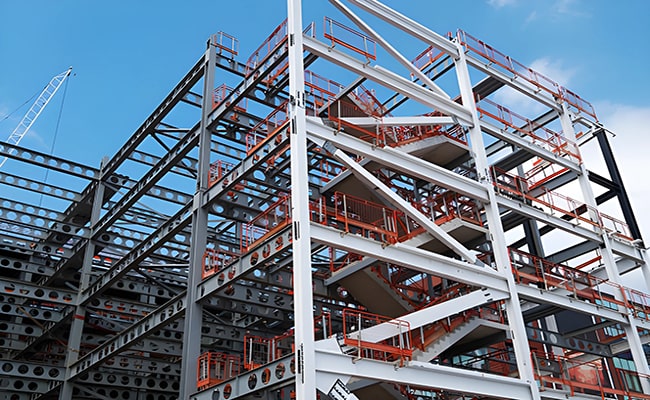

2. Portal Frame: Pillar of Industrial Buildings
A portal frame is a single-layer structure with a rigid connection between steel columns and beams. It is mainly used for large-span buildings such as industrial workshops, warehouses, hangars, and gymnasiums. The portal frame uses steel in a shape similar to the letter “H”, with purlins and bracing systems, to form a stable structural system with a simple structure, light weight, reasonable force, and convenient construction.
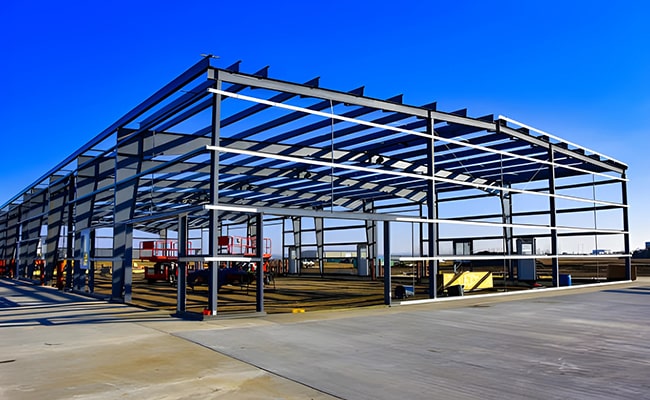

3. Truss system: maximizes strength with minimal materials
The truss uses the stability of the triangle and is composed of the upper chord, lower chord, and web. A higher bearing capacity is achieved with less material through the reasonable arrangement of the rods. This structure is often used in large-span buildings such as bridges and roofs, such as stadiums and terminal roofs, and is usually composed of large-span tube trusses. The truss structure is light in weight and effectively disperses the load, reducing the pressure of the structure on the foundation, so the material and foundation construction costs are low.
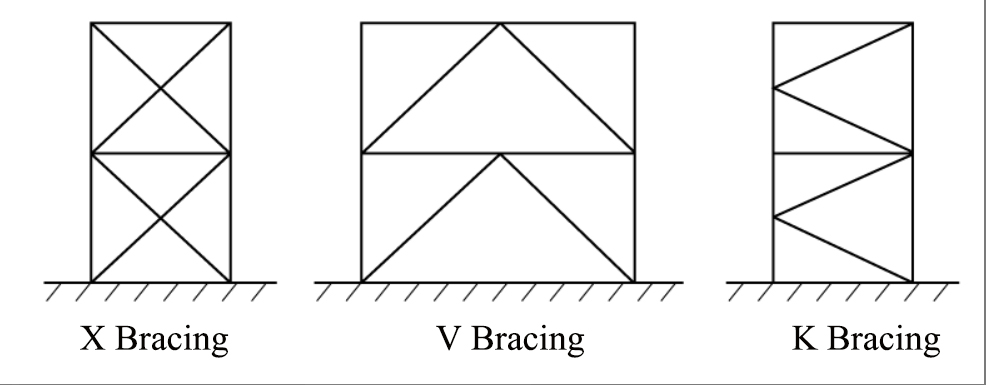
4. Bracing frame: Enhance structural integrity
The bracing frame usually comprises frame and bracing, which jointly bear vertical and horizontal forces. This structure can effectively resist wind loads and earthquakes and enhance its stability. Common bracing types include X-shaped, K-shaped, and V-shaped bracing, which have the characteristics of a flexible layout and lateral resistance.
Design stage: Planning steel frame structure
Structural engineering and load considerations
Engineers use calculations and model analysis during the steel frame design stage to ensure the building can withstand various external loads, including dead, live, wind, snow, and earthquake. They also reasonably distribute the loads to ensure the structure is safe and stable under stress. In addition, the structure’s high temperature and corrosion resistance should also be considered to extend the service life and reduce the cost of later maintenance.
Choose the correct steel grade and section.
The appropriate steel grade should be selected according to the building specifications during the design. The steel frame structure mainly uses Q355B, a low-alloy high-strength structural steel, to ensure its durability. In addition, the cross-sectional specifications of the steel also directly affect the stress performance of the steel frame. The box structure has a stronger deformation resistance than H/I-shaped steel for super-large spans and super-high buildings, so it has higher strength and stability.
Understand the load path and stress distribution.
The stability of the steel frame structure depends on the load path design; that is, the load acting on the building is transferred to the foundation. Engineers need to analyze the structure’s stress to ensure that the load is evenly distributed on the columns, beams, supports, and foundations to avoid concentrated stress and damage to the structure. In addition, stress distribution analysis can optimize the node connection method, such as welding and bolting, to enhance the stability of the overall structure.
Selection of steel frame materials: hot-rolled steel and cold-bent steel
Steel is mainly divided into two types: hot-rolled steel and cold-bent steel. Hot-rolled steel is steel made by rolling steel billets at high temperatures. It performs better in terms of strength, toughness, and rigidity and is suitable for load-bearing structures, such as steel columns, beams, and large-span trusses. Cold-bent steel refers to profiles made of strip steel and processed by pressure at room temperature. Also known as thin-walled steel, it is a type of light building structural steel, such as roof purlins and wall beams. The choice of steel depends on the needs of the project. Hot-rolled steel is the first choice for large-span, high-load buildings, while cold-bent steel has more advantages for light buildings with low loads.
Conclusion
Steel frame structures play an irreplaceable role in modern buildings. They can provide superior bearing capacity and durability for high-rise buildings, industrial warehouses, bridges, or stadiums. Through reasonable design, precise manufacturing, and high-standard construction technology, steel frame structures can meet complex building needs and achieve the best balance in safety, durability, and economy.














