A steel frame is a structure made of steel, usually connected by welding, bolting, or riveting steel beams, columns, bracing,…
Steel structure bolt connect more than two steel structure parts or components into one. Bolt connection is the easiest connection method in steel structure pre-assembly and installation.
Bolt connection was first used in metal structure installation. In the late 1930s, the bolt connection was gradually replaced by the rivet connection, which was only used as a temporary fixing measure in component assembly. In the 1950s, high-strength bolt connection methods appeared. High-strength bolts are made of medium- or medium-carbon alloy steel, and their strength is 2 to 3 times higher than ordinary bolts. High-strength bolt connection has the advantages of convenient construction, safety, reliability, etc. It has been used in manufacturing and installing steel structures in some metallurgical factories since the 1960s.
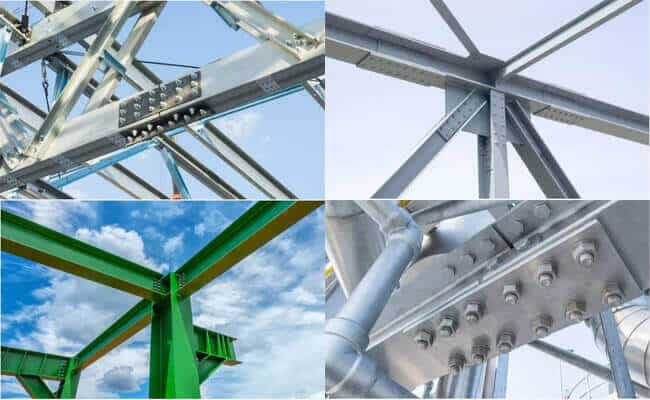

Classification of steel structure bolt
Bolts have many names, such as screws, bolts, standard parts, fasteners, etc. A bolt is a general term for a fastener.
In a broad sense, bolts include ordinary bolts, high-strength bolts, anchor bolts, expansion bolts, chemical anchors, etc. In a narrow sense, bolts are divided into ordinary bolt connections and high-strength bolts.
Ordinary steel structure bolt
Mainly divided into rough bolts and refined bolts.
According to the form, ordinary bolts can be divided into hexagon head bolts, stud bolts, countersunk head bolts, etc.,
According to the production accuracy, it can be divided into three grades: A, B, and C grades. A and B grades are refined bolts, C grades are rough bolts, and connecting bolts for steel structures are generally ordinary rough C grades unless otherwise specified.

Coarse bolts
It is made of carbon-structural steel. In order to make the bolt penetrate the screw hole smoothly, the hole diameter should be 1.0~2.0mm larger than the nominal diameter d of the bolt. The distance between the bolt holes should be arranged so the wrench can easily tighten the nut. When rough bolts are used for the connection of columns, beams, and roof trusses, the connection structure of supporting plates shall be adopted. The bolt is under tension at this time, and the supporting plate bears its shear force.
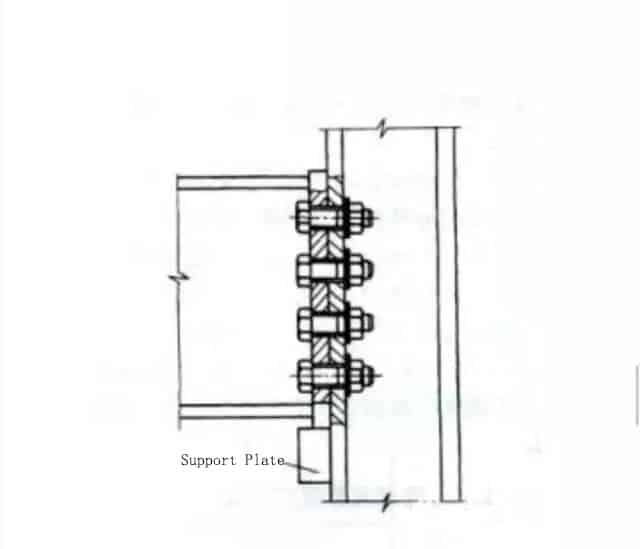
The low-strength grade of the material used for crude bolts limits its scope of use in structural connections, but it can still be used in the connection of secondary beams of working platforms, wall skin beams, roof beams and supports, and hinged supports with small shear forces.
Coarse bolts are also widely used in the pre-assembly of steel structures, pre-tightening of riveted components before riveting, assembly before high-strength bolt connections, and temporary fastening before welding installation nodes. When rough bolts are used as permanent fixing bolts, they need to be tightened after alignment, and anti-loosening measures should be taken.
Refined bolts
The diameter of the hole is the same as the diameter of the screw. When the bolt penetrates the screw hole, it should be hammered. The quality of the hole and the machining accuracy of the screw must be strictly required. Refined bolt connections are used for structural connections that are often disassembled and cannot be riveted. Refined bolts are generally used in mechanical products and are rarely used in steel structure buildings.
Refined bolts
The diameter of the hole is the same as the diameter of the screw. When the bolt penetrates the screw hole, it should be hammered. The quality of the hole and the machining accuracy of the screw must be strictly required. Refined bolt connections are used for structural connections that are often disassembled and cannot be riveted. Refined bolts are generally used in mechanical products and are rarely used in steel structure buildings.
High-strength Steel structure bolt
High-strength bolts are high-strength steel that requires a large pre-tightening force. High-strength bolts apply pre-tensioning force and transmit external force by friction. Ordinary bolt connection transmits shear force by the shear resistance of the bolt rod and the pressure bearing of the hole wall. When the nut is tightened, the pre-tension force is very small, and its influence can be ignored. In addition to its high material strength, the high-strength bolt also exerts a large pre-tensioning force, produces extrusion force between the connecting components so that there is a large friction force perpendicular to the direction of the screw, and the pre-tensioning force, anti-slip coefficient and steel type all directly affect the bearing capacity of high-strength bolts.
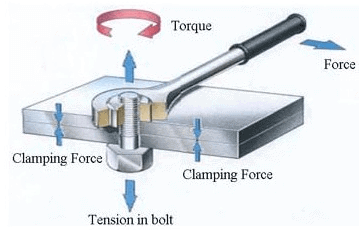
High-strength bolts are divided into two types according to their stress conditions: friction and pressure-bearing.
According to construction technology, high-strength bolts are divided into torsional shear high-strength bolts and large hexagonal high-strength bolts.

Friction-type high-strength bolt:
The external force is transmitted by the friction force generated on the contact surface of the steel plate after the bolt tightening pressure makes the connection plate close. After sandblasting the surface of the component, a red rust surface can be obtained, which can obtain a larger friction coefficient and reduce the number of connecting bolts. The hole diameter of friction-type high-strength bolts should be 1.5-2.0mm larger than the nominal diameter d of the bolts.
Pressure-bearing high-strength bolt:
It is to transmit stress by making the frictional force generated between the components and the shear force of the central axis of the bolt act simultaneously with the bearing pressure of the component, and its hole diameter should be 1.0 larger than the nominal diameter of the bolt d ~1.5mm. Holes are drilled using CNC drilling machines and drilling templates.
In short, friction-type high-strength bolts and pressure-type high-strength bolts are the same kinds of bolts, but whether the design considers slippage or not. Friction-type high-strength bolts must not slide, and the bolts do not bear shear force. Once they slip, the design considers that they have reached a destructive state, which is relatively mature in technology; pressure-bearing high-strength bolts can slide, and the bolts also bear shear force, and the final failure is equivalent to that of ordinary bolts. Bolt damage (bolt shearing or steel plate crushing).
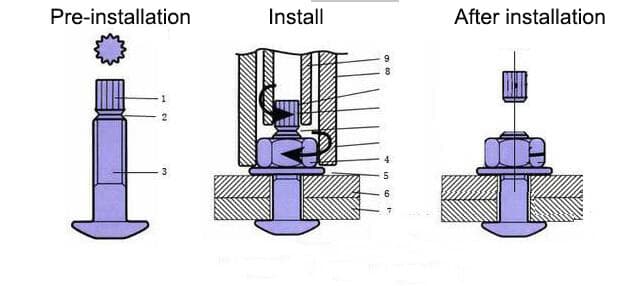
Large hexagonal high-strength bolts
consisting of a high-strength bolt, a nut, and two washers, can form a high-strength bolt connection pair.
During construction, use rough bolts to fix the structure temporarily. After the structure is installed and aligned, replace the rough bolts with high-strength bolts one by one from the middle of the bolt group and perform initial tightening. After the initial tightening, retighten in sequence and final twist.
When installing large hexagon head high-strength bolts, a washer should be added on both sides of the bolt The initial tightening torque value is 50% of the final tightening torque value, the retightening torque value is equal to the final tightening torque value, and the calculation formula of the final tightening torque value is Tc=KPcd. In the formula, Tc is the final tightening torque value, N m; K is the torque coefficient; Pc is the construction pretension, kN; d is the thread diameter of high-strength bolts, mm. The torque wrench is used for tightening, and torque correction should be performed before each use.
Torsional shear high-strength bolts
A high-strength bolt, a nut, and a washer form a torsional shear type high-strength bolt connection pair.
When installing a torsional shear-type high-strength bolt connection pair, a washer should only be added on one side of the nut. The formula for calculating the initial torque value is Tc=0.065Pcd. In the formula, Tc is the initial tightening torque value, N.m; Pc is the construction pretension, kN; d is the thread diameter of high-strength bolts, mm. Finally, use a special wrench to twist the torx head at the end. The focus of quality inspection should be on the supervision and inspection of the construction process.
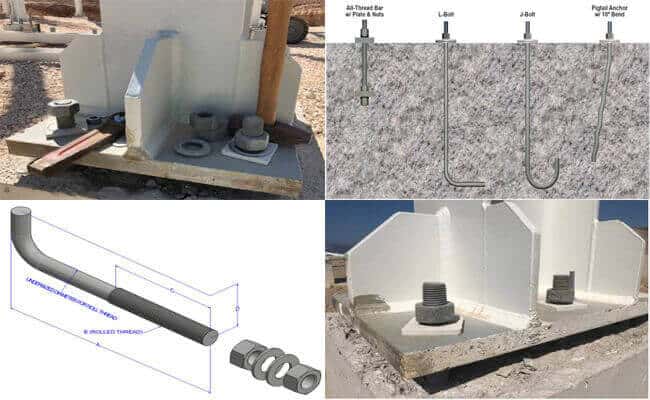
Anchor bolts
Anchor anchor bolts, anchor bolts, anchor screws, anchor wires, etc., connect the steel structure column foot and the concrete foundation. Generally, it is made of Q235B and Q355B steel rods.
During installation, the anchor bolt group is fixed by the steel frame and installed with the binding steel cage, and then concrete is poured, and the bolt head should be exposed to a certain length of the concrete surface. After the concrete reaches a specific strength, the steel column foot is installed, and finally, the column base is grouted for the second time.
Chemical anchors
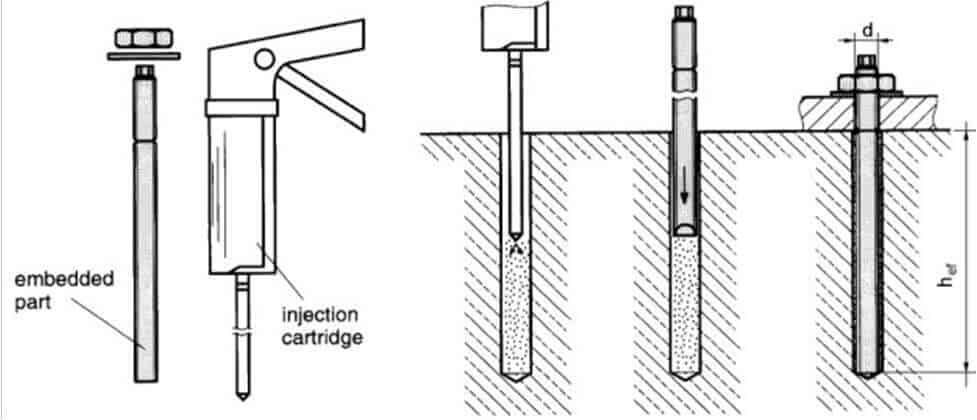
The chemical anchor is a new type of fastening material composed of chemical agents and metal rods. Connectors for installing other structures on existing concrete structures. It can be used for the installation of post-embedded parts in various steel structures, curtain walls, and marble dry-hanging constructions. It can also be used for equipment installation, road and bridge guardrail installation, and building reinforcement and transformation.
The chemical anchor bolt is a new type of anchor bolt that appeared after the expansion anchor bolt. It is a composite part that is fixed in the drill hole of the concrete base material through a special chemical adhesive and screw cement to realize the anchorage of the fixing part. Because the chemical anchor bolt has a large pull-out bearing capacity, it can replace the anchor bar of the embedded part. It is often used to remedy the situation where the steel structure embedded part is forgotten to be installed, but the concrete has been poured.
The construction steps of chemical anchor bolts are as follows:
(1). According to engineering design requirements, holes should be drilled at corresponding positions in the base material (such as concrete). Professional technicians or field tests should determine the hole diameter, depth, and bolt diameter.
(2) Drill holes with a percussion or water drill.
(3). Use a special air cylinder, brush, or compressed air machine to clean the dust in the drilled hole. It is recommended to repeat it no less than 3 times. There should be no dust and clear water in the hole.
(4). Ensure that the bolt surface is clean, dry, and free from oil.
(5). Confirm that the glass tube anchoring package has no abnormalities such as appearance damage and agent solidification, put its round head outward into the anchoring hole, and push it to the bottom.
(6). Use an electric drill and a special installation fixture to forcefully rotate the screw and insert it into the bottom of the hole. The impact method should not be used.
(7). When it is screwed to the bottom of the hole or the mark position on the bolt, stop the rotation immediately, remove the installation fixture, and avoid disturbance after gelation until it is completely cured. Overtime rotation causes glue loss and affects anchoring force. (The rotation time should not exceed 30 seconds, the rotation speed should not be lower than 300 rpm, not more than 750 rpm, the bolt advancing speed should be about 2cm/s, and the impact method is not allowed.)
Expansion bolts
Expansion bolts have the same function as chemical anchors and are used for anchors with less stress.
Expansion bolts shall not be used in the parts of the concrete structure that have cracks and the parts that are prone to cracks. At the same time, the expansion bolts used in the design of main load-bearing structures, critical pipelines, high-speed operation, impact load, and vibration should be selected according to the calculated design tensile force and design shear force.

Materials and specifications of steel structure bolt
The specifications of steel structure bolt commonly used are M12, M16, M20, M24, and M30, M is the bolt symbol, and the number is the nominal diameter.
Steel structure bolt divided into ten performance grades: 3.6, 4.6, 4.8, 5.6, 5.8, 6.8, 8.8, 9.8, 10.9, and 12.9. The bolts above grade 8.8 are made of low-carbon alloy steel or medium-carbon steel. They have been heat-treated (quenched, tempered, etc.) fire), commonly known as high-strength bolts, and below grade 8.8 (excluding grade 8.8) are commonly referred to as ordinary bolts.














