In the construction of modern storage facilities, steel structure warehouses have become one of the mainstream building forms due to…
The design of steel structure workshop is tailored to its use function to ensure smooth material flow and efficient use of internal space. The operational requirements of the workshop determine its size and layout.
The site selection of a steel structure workshop should fully consider the local terrain, traffic, and environmental factors. A strengthening design must be adopted if the workshop is located in an area with strong winds or frequent earthquakes. In addition, the design of steel structure workshops must comply with building specifications to ensure that the structure meets the load requirements and improves the stability and safety of the overall structure.
The attention to the design of steel structure workshop:
Load-bearing of steel workshop building
The structural safety of steel structure workshops depends on their load-bearing capacity. The calculated and designed steel frame structure can ensure that the workshop can withstand wind loads, snow loads and earthquakes. The load-bearing capacity of the workshop depends on the load-bearing structure and load.
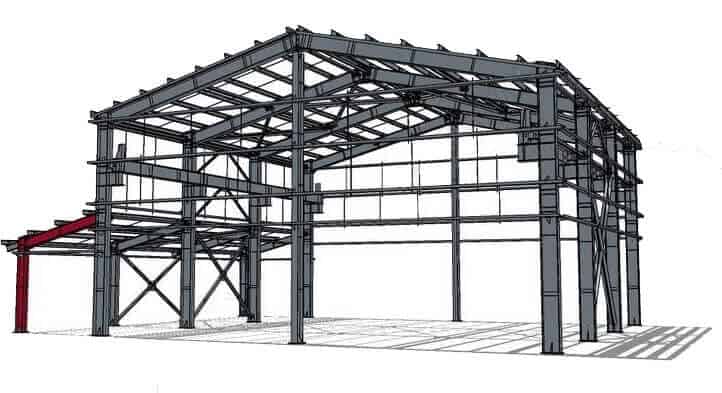
Main load-bearing structures:
Steel columns: bear vertical loads and transfer them to the foundation. H-shaped steel or box-shaped steel is usually used to improve strength and stability.
Steel beams: support roof loads and disperse pressure. H-shaped steel is commonly used. If the span is large, a truss structure can be used.
Roof truss: This supports the roof panel and resists wind load. Angle steel truss or square tube truss can be used. The truss is lightweight and has a strong bearing capacity, making it suitable for large-span workshops.
Bracing system: This includes column, roof, and wall bracing, which enhances the steel workshop building’s wind and earthquake resistance and prevents structural deformation.
Load classification:
Constant load: the dead weight of the steel structure factory building, including steel components, roof and wall panels, etc.
Live load: variable load caused by personnel activities and equipment operation changes.
Wind load: the effect of wind on the workshop, which is related to wind speed.
Snow load: for cold areas, snow accumulation will produce additional pressure on the roof, so the design of steel structure workshops must calculate snow load.
Earthquake load: horizontal and vertical forces caused by earthquakes.
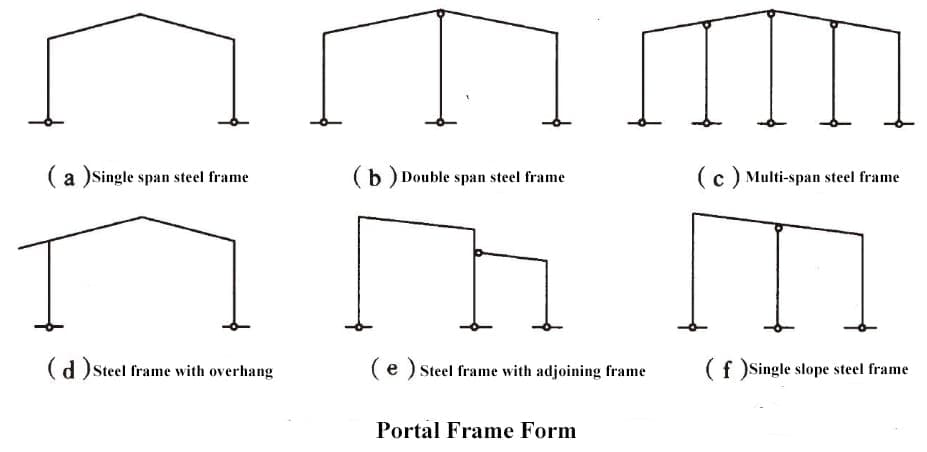
Portal steel frame design:
There are various forms of portal frames, and common types include single ridge single slope, multi-ridge multi-slope, and single ridge double slope multi-span. In addition, depending on the specific functional requirements and building conditions, overhanging eaves or adjacent frames can also be used to adapt to different spatial layouts and usage requirements.
Stability is the key to the design of portal steel frame, which determines the lateral displacement resistance of the steel frame under wind load and earthquake. Stability can be achieved by setting up a support system and increasing the stiffness of the column foot.
Deflection refers to the deformation of steel beams in large spans, which affects the safety of the structure. Deflection control can be optimized by increasing the cross-sectional size. For steel structure workshops with cranes, the torsional force of steel columns should be considered. Tie rods can be set between steel columns and beams to increase torsional resistance.
The structural form of the steel structure workshop:
Portal steel frame usually adopts variable section design. The structure can achieve the best load-bearing effect in different stress areas through reasonable section height change, reduced steel consumption, optimized materials, and improved structural stress. However, when the factory needs to install a crane, the column usually adopts a uniform section design to provide a more uniform stress state and stronger bending resistance to ensure the stability of the structure during the operation of the crane, reduce vibration and displacement, and improve safety and service life.
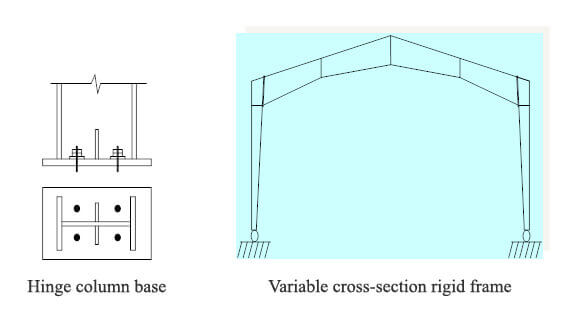
The column foot usually adopts a hinged design to reduce the transmission of bending moment at the column foot, reduce the requirements of foundation stiffness, simplify the foundation design, and reduce construction costs. This design is suitable for steel structure workshops without cranes. For factories with cranes, the column foot adopts a rigid connection design. The rigid column foot can withstand more incredible bending moments, enhance the stability and bearing capacity of the structure, and reduce the displacement of the steel column during the operation of the crane.
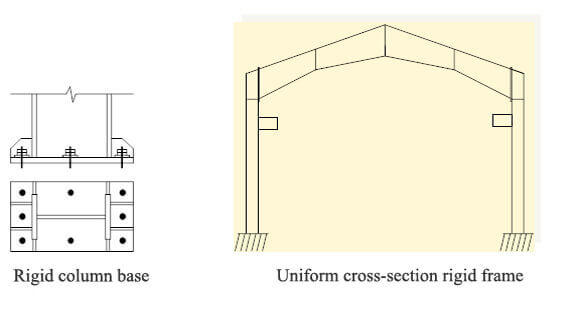
Standards for force analysis of portal frames
Steel structure workshops have a variety of configurations, each of which can meet specific functional and spatial requirements. Common forms include single-span, multi-span, and multi-story workshops. Single-span workshops provide unobstructed internal space, ideal for manufacturing processes requiring a lot of mechanical movement. Multi-span structures use additional internal columns to support a more expansive layout, while multi-story designs maximize vertical space efficiency. Choosing the proper structural form is essential for operational efficiency and long-term sustainability.
In structural calculations, roof live loads are usually assumed to be fully distributed loads. The larger the load value, the higher the safety, but the corresponding amount of steel will also increase. Therefore, setting load standards reasonably is essential to ensure structural safety and economy.
According to the code requirements, for light roofs using corrugated steel sheets, the standard value of the live load in the vertical direction of the roof should be 0.5kN/m², which applies to the calculation of roof panels and purlins. However, when the horizontal projection area of the steel structure exceeds 60m², the roof’s vertical uniform live load value shall not be less than 0.3kN/m² to ensure the safety of large-span structures.
Steel structure workshop designs must comply with strict stress analysis standards. Structural engineers usually use finite element analysis to simulate stress distribution and identify potential weak points, including bending moment, shear force, axial load, and other factors. The design must also comply with building codes to ensure the steel frame will not deform or be displaced when bearing external loads.
The load effect combination must meet the following standards:
Steel structure workshop design must withstand multiple load combinations, including:
Static load + live load – evaluate the combined effects of permanent and variable forces.
Static load + wind load – ensure lateral stability under high-speed wind.
Static load + seismic load – enhance seismic resistance through ductile details.
Static load + snow load – prevent snow accumulation from causing excessive roof deflection.
Each load combination must meet the requirements of building codes to ensure safety and durability.
Step for steel structure workshop design:
Steel structure workshop design systematically involves multiple links from initial planning to final construction.
1. Site Analysis
The site must be evaluated to ensure the structural design meets the geographical and environmental conditions before the steel structure workshop design. Site analysis includes the following factors:
Climatic conditions: Evaluate the local wind speed and snowfall, as well as the temperature range, to determine the wind load, snow load, and insulation requirements.
Seismic activity: If the project is in an earthquake-prone area, the seismic force must be calculated, and the steel structure workshop design follows the seismic code.
Foundation bearing capacity: The soil needs to be explored and the foundation bearing capacity calculated before the foundation design.
2. Conceptual design
The overall structure of the steel structure workshop is determined in the conceptual design stage, including:
Structural design: Select single-span, multi-span, or multi-layer frame structures to meet the use requirements of different types of workshops.
Spatial layout: Plan the spatial layout according to the production process requirements and the equipment layout to improve production efficiency.
3. Material selection
The selection of steel directly affects the bearing capacity and durability of the workshop. The following factors are mainly considered:
Strength requirements: According to load calculations, appropriate steel materials are selected. The main structure uses Q355B high-performance steel, and the secondary structure uses Q235B steel.
Surface treatment: Select appropriate surface treatment processes according to the surrounding environment. The conventional surface treatment method is spray painting. If it is in a humid or corrosive environment, hot-dip galvanizing is required to extend the service life of the steel structure plant.
4. Structural calculation and modeling
Use advanced engineering software for precise calculations and structural analysis to ensure that the design meets the requirements of building specifications.
Finite element analysis: Simulate the stress conditions of steel structures under different loads (e.g., wind loads, snow loads, seismic forces), and predict structural deformation and stress concentration areas.
Stability analysis: Calculate the deflection and buckling that may occur in the structure under the combined action of loads and optimize the design.
5. Detailed structural design
A detailed design is required after completing the structural calculation, and architectural and structural drawings are prepared.
Node design: Optimize beam-column connections, support systems, and bolt arrangements to improve overall stability.
Structural drawing: The structural drawing includes the basic structure drawing of the steel structure plant, plan and elevation drawings, overall layout, component details, and node details.
The Lighting for the design of the steel structure workshop
The area of steel structure workshops is vast, and lighting is also a big problem. Especially in some industrial workshops, light is an essential facility. Improve indoor lighting through daylighting panels during the day to save energy.

When arranging daylighting panels or glass at specific locations of the metal roof. The service life of the skylight should be the same as that of the metal roof panel. The waterproof treatment should be applied at the junction of the daylighting panel and the metal roof sheet.
Moisture-proof
Summer is a rainy season. To prevent water vapor from the bottom of the metal roof, it is necessary to remove the water vapor from the metal roof.
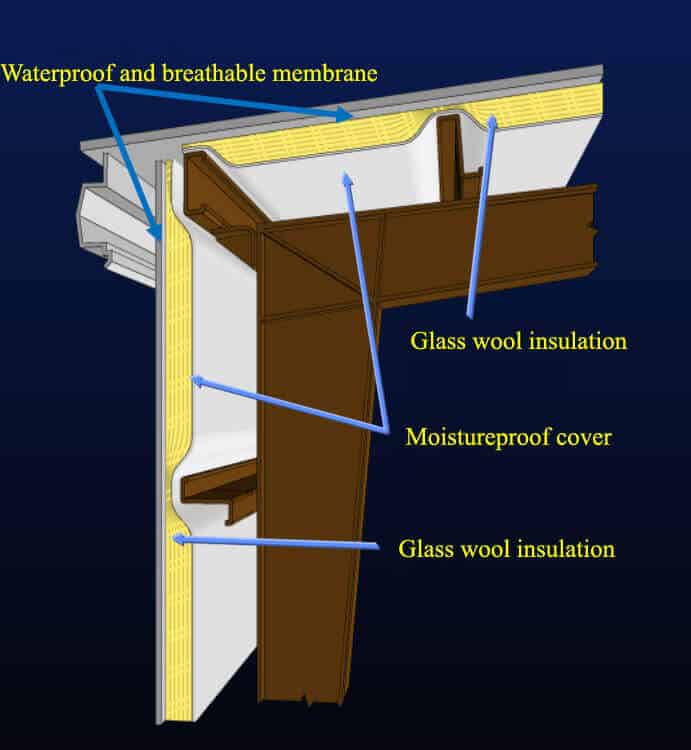
The metal roof layer should be filled with insulation cotton, and the metal roof bottom sheet should be laid with a waterproof film. They are ventilable on the metal roof, which will be moisture-proof for the steel structure workshop.
Fireproof for the design of steel structure workshop
The design of the steel structure workshop needs to consider the fireproofing design. During the use of a steel structure workshop, there is a significant hidden danger of a fire disaster.

When the components of the steel structure workshop exceed a specific temperature, the strength and yield strength of the parts will decrease, which can easily cause collapse accidents.
Therefore, the steel structure workshop needs to be sprayed with fireproof materials, which can improve the fire resistance of the construction in the event of a fire.
Sound insulation
During the production and construction process, noise will be generated inevitably. The steel structure of the factory building prevents sound from being transmitted indoors and outdoors.
Fill the metal roof layer with sound insulation material (usually made of insulation cotton), and the sound insulation effect is expressed by the difference in good intensity on both sides of the metal roof.
The sound insulation effect is related to the density and thickness of the sound insulation material. It should be noted that sound insulation materials have different blocking effects on the sounds of different frequencies.
Thermal Insulation
Steel structure workshop design should also pay attention to the issue of thermal insulation. If the steel structure workshops are built in cold regions, they must consider heat preservation in winter.

The thermal insulation function is realized by filling thermal insulation materials (commonly used glass wool and rock wool) under the metal roof panel.
The thermal insulation performance is determined by the following factors: the raw material, density, and thickness of the thermal insulation cotton. The humidity of the thermal insulation cotton, the connection method of the metal roof panel, and the underlying structure(to prevent the “cold bridge” phenomenon). The ability of the metal roof layer to heat radiation was repeated.














