In the construction of modern storage facilities, steel structure warehouses have become one of the mainstream building forms due to…
The construction of a steel structure foundation is essential in construction projects. The quality of its construction directly affects the quality and level of project construction, so we must pay attention to it.
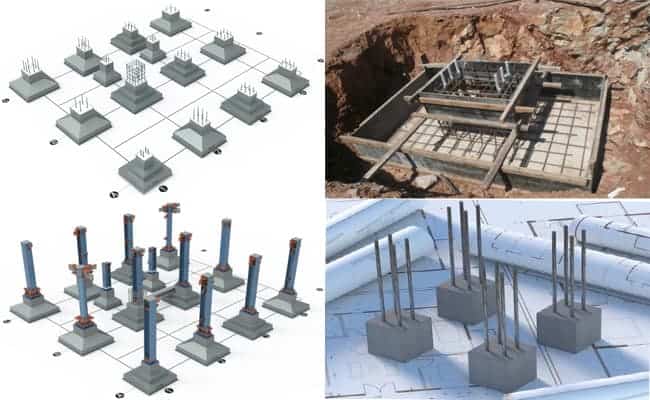
Steel structure foundation:
What is a steel structure foundation?
A steel structure foundation supports and secures steel structure columns or trusses and transfers their weight to the ground. It is a reinforced concrete structure with a column base, cap, column, and embedded bolts or steel plates.
There are three types of steel structure foundations: stepped foundations, sloped foundations, and cup-shaped foundations.
Slope-type Steel structure Foundation
Step-type Steel Structure Foundations
Steel structure foundation construction process:
Construction sequence:
Cleaning the foundation pit and leveling → concrete cushion → Foundation laying → Steel bar binding → related professional construction → Cleaning → supporting formwork → Cleaning → concrete mixing → concrete pouring → concrete vibrating → concrete leveling → concrete curing → formwork removal.
1. Clean the foundation pit and level it

Cleaning the foundation pit removes surface floating soil and disturbed soil without leaving any accumulated water. Leveling is to make the bottom elevation of the foundation meet the design requirements. Before constructing the foundation, the bottom elevation of the foundation should be determined on the base surface.
2. Cushion construction

After the foundation groove inspection, cushion concrete construction should be carried out immediately. A C10 fine stone concrete cushion should be poured on the base surface. The cushion concrete must be vibrated densely, and the surface should be smooth. Drying the base soil is strictly prohibited. The underlayment is constructed to protect the foundation’s steel bars.
3. Positioning and laying out:
Use a total station to lay out all independent foundations’ center and control lines.
4. Binding steel bars
After the cushion pouring is completed and the concrete reaches 1.2MPa, the surface elastic lines bind the steel bars. Steel bar leakage is not allowed in the steel bar binding.
The hook part of the column insertion bar must be tied at 45° to the bottom plate reinforcement, and all connection points must be tied.

The first stirrup is tied 5cm away from the bottom plate, and the last stirrup is tied 5cm away from the top of the foundation as the elevation control bar and positioning bar.
Another positioning bar is tied at the top of the column insertion bar. The upper and lower stirrups and positioning stirrups are tied up.
Finally, adjust the column reinforcements in place and temporarily fix them with a tic-tac-toe wooden frame, and then tie the remaining stirrups to ensure that the column reinforcements do not deform. The two positioning bars must be replaced after the foundation concrete is poured.
When the side length of the reinforced concrete independent foundation under the column is greater than or equal to 2.5m, the bottom plate stress reinforcement length can be 0.9 times the side length and should be arranged staggered.
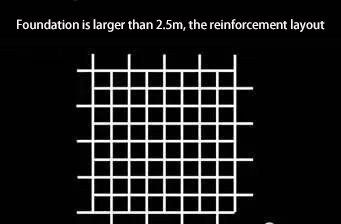
After the steel bars are tied, protective layer pads are placed on the bottom and sides. The thickness is the designed protective layer thickness. The spacing between the pads shall not be greater than 100mm (determined by the designed steel bar diameter) to prevent the common quality problem of exposed bars.
5. Template
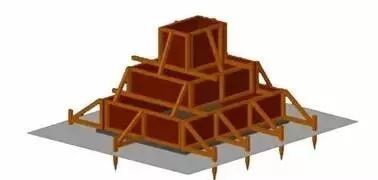
The formwork adopts small steel or wooden molds and is reinforced with shelf tubes or wooden squares. For the stepped independent foundation, each step formwork is made according to the size of the foundation construction drawing, and the formwork is installed layer by layer from bottom to top.
6. Clean up
Remove sawdust, soil, and other debris from the formwork, water the wooden formwork to moisten it, and seal the seams and holes in the boards.
7. Concrete pouring
Concrete should be laid continuously in layers, and the intermittent time should not exceed the initial setting time of concrete, generally not more than 2 hours. To ensure the correct position of the steel bars, a layer of 5 to 10cm thick concrete should be poured first to fix them. The step-type foundation is poured as a whole at the height of each step. After each step is poured, pause for 0.5 hours and wait for it to sink before pouring another layer.
When pouring concrete, always observe whether the formwork, brackets, steel bars, bolts, reserved holes, and pipes are moving. Once any deformation, movement, or displacement is found, stop pouring immediately, repair and strengthen the formwork in time, and continue pouring.
8. Concrete vibration
When using a plug-in vibrator, the distance between insertions should not exceed 1.25 times the length of the active part of the vibrator. The upper vibrator is inserted into the lower layer 3 to 5cm. To prevent embedded parts from shifting, avoid collisions with embedded parts and embedded bolts.
9. Concrete leveling
After pouring the concrete, use a flat vibrator to vibrate it with a relatively large surface, then use a scraper to smooth it, and then use a wooden trowel. The concrete surface elevation must be checked before closing, and any areas not meeting the requirements should be rectified immediately.
10. Concrete maintenance
The poured concrete should be covered and watered in about 12 hours. Normal curing at average temperature shall not be less than seven days, and curing of special concrete shall not be less than 14 days. Devoted personnel shall inspect and implement maintenance to prevent cracks on the concrete surface caused by untimely maintenance.
11. Template removal
The side formwork can only be removed when the strength of the concrete ensures that its edges and corners will not be damaged by removing the formwork. Before removing the formwork, assign a dedicated person to check the strength of the concrete. When dismantling, use a crowbar to remove it sequentially from one side. Sledgehammers or crowbars are not allowed. Pry randomly to avoid damaging the edges and corners of the concrete.
Common problems with steel structure foundation construction quality
1. Waterproofing of foundation side elevation
The basic waterproof layer needs to be a protective layer. The foundation floor surface is a 40~50mm thick fine stone concrete protective layer, and the surface of the waterproof layer of the side elevations, such as foundation beams and water collection pits, is generally covered with 20mm thick cement mortar as a protective layer. Once the quality of the protective layer is not up to standard, or no protective layer is used, it will seriously affect the foundation’s bearing capacity and service life.
2. Dimensional deviation of foundation trench (pit)
3. Base elevation error
4. Backfill soil density is unqualified.
5. Backfill quality does not meet the requirements.
6. The basic appearance is unqualified.
Steel structure foundation construction notes
(1) When pouring the stepped foundation, attention should be paid to preventing voids and honeycombs (i.e., hanging legs and rotten necks) in the concrete at the intersection of the upper and lower steps. To avoid such phenomena, wait 0.5 seconds after pouring the first step. ~1h, wait for the lower part to sink solidly, then pour a step to prevent it effectively.
(2) When pouring the cup-shaped foundation, attention should be paid to the elevation of the cup bottom and the position of the cup mouth mold to prevent the cup mouth mold from floating and tilting. First, vibrate the concrete at the bottom of the cup mouth, stop for a moment, wait for it to sink, and then pour the concrete around the cup mouth mold symmetrically and evenly.
(3) When pouring a tapered foundation, formwork is not required if the slope is relatively flat, but attention should be paid to the compaction of the concrete at the hill and corners. After the vibration, the slope surface can be corrected, flattened, and compacted manually.
(4) If the groundwater level in the foundation pit is high during foundation concrete pouring, measures should be taken to reduce the groundwater. The precipitation should not be stopped until the foundation pit backfill is completed to prevent the foundation from soaking and causing uneven settlement, tilt, and cracks.
(5) After removing the foundation formwork, the soil should be backfilled in time. The backfilling should be carried out evenly on the opposite sides or around the surroundings simultaneously and compacted in layers to protect the foundation and facilitate the following process.














