When designing pre-engineered steel factory buildings, it‘s essential to consider the height and span of the steel factory. These factors…
In architecture, the diversity and complexity of structures have always been inevitable challenges. The choice of building structures, classified by material or number of layers, directly affects the building’s performance, safety, and usability.
This article will delve into the basic types of building structures, from material division, to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding and help us better understand and appreciate the complex technologies and techniques involved in construction projects. Let’s explore the world of architectural structures and explore their subtleties.

Building structures are divided according to materials.
1. Steel structure
Steel structures can build various types of systems that reinforced concrete can make. They have the advantages of being lightweight, fast construction, and good earthquake resistance. They are especially suitable for large-span and high-rise structures.
At present, steel structures are mainly used in four aspects: First, portal steel structures, such as warehouses, factories, hangars, etc.; Second, in frame structures, such as multi-story or high-rise buildings; Third, grid frames and lattice shells; The Fourth is the cable-membrane structure.

2. Mixed structure
It is widely used in multi-story buildings with few floors. The so-called mixed structure refers to using two or more different materials in the same building structures system to form a load-bearing structure. It generally refers to a load-bearing structural system composed of reinforced concrete houses, floors, and brick walls, so it is also called a brick-concrete structure.

Mixed structures are widely used in buildings with few floors because they have the advantages of lower cost and lower requirements on construction technology and construction equipment. Mixed systems also have certain disadvantages. Since the strength of brick masonry is relatively low, the number of floors of the building is limited when using brick walls to bear a load. The disadvantages of Mixed structures include poor integrity and poor earthquake resistance.
3. Reinforced concrete frame
Reinforced concrete is used as a structural material. The frame can also use steel frame, but currently, reinforced concrete is mainly used to build the frame, so the reinforced concrete frame structure is often referred to as the frame structure.
A frame is a skeletal structure rigidly connected by beams and columns. The rigid connection of beams and columns can fully use the bending resistance of slender members such as beams and columns. It can also make beams and columns work together to resist vertical or lateral loads, making the structural stress more reasonable than hybrid structures.

The frame structure only has columns in the vertical direction, unlike the hybrid system, which has many internal load-bearing walls. Therefore, the frame building structures use function is more flexible and suitable for residential and prominent public buildings. Frame structures also have better seismic performance than hybrid structures. Frame structures are more expensive than hybrid structures. It is often used to build multi-story houses up to 10 stories.
4. Frame shear structure
Shear walls can also use steel structures. When the building is tall, the lateral wind and earthquake effects are substantial, and the slender beams and columns of the frame structure cannot withstand it. At this time, if you thicken the beams and columns, it will not be economical on the one hand, and it will also affect the use function of the house.
The frame shear structure solves this problem better. In the frame-shear construction, in addition to the beams and columns of the frame, a certain number of cast-in-situ reinforced concrete walls are also added at appropriate locations, called shear walls. Shear walls can significantly improve a structure’s ability to resist wind and seismic actions;
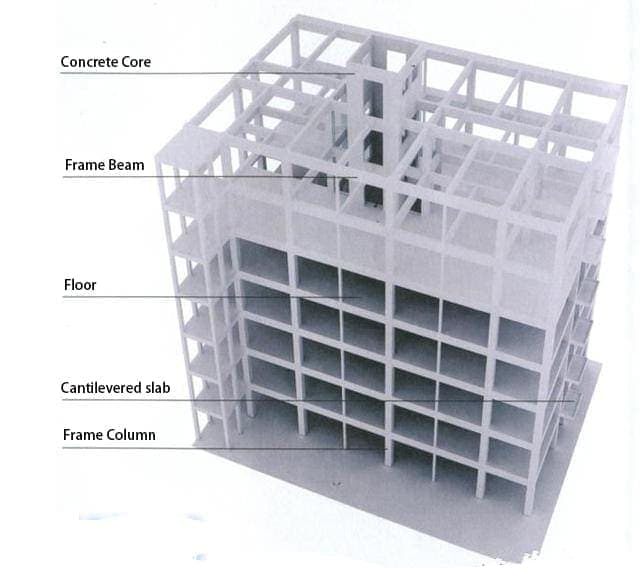
Properly installed shear walls will not affect the functionality of the house. Reinforced concrete frame-shear structures can be used to build homes with 10-25 floors. Most “small high-rise buildings” around 20 feet in China are of frame-shear form or mainly frame-shear design.
5. Concrete shear wall structure
There are no beams and columns in the shear wall structure, and all shear walls are used to support the floor slabs, so it is also called an entire shear wall structure.
Shear walls are thin and cannot withstand large concentrated forces, so full-shear wall structures generally use slab floors. This structure has many shear walls and good resistance to lateral wind and earthquake effects.
Its disadvantage is that the span of the floor limits the spacing of shear walls; the number of shear walls is large, and the use functions of the house are limited. Complete shear wall structures can be built higher than frame shear designs but are generally only suitable for buildings with smaller rooms, such as residences and hotels.
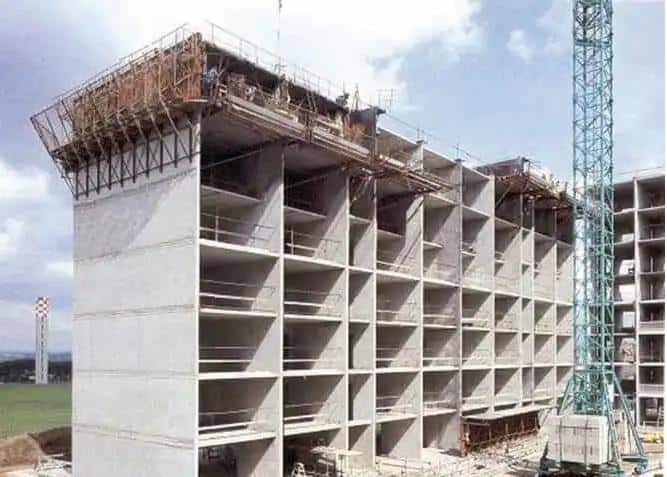

The building structures are divided according to the number of floors
1. Multi-layer structure
Multi-story structures account for a large proportion of house structures; for example, many residential buildings, hotels, office buildings, hospitals, schools, and other civil buildings, as well as industrial buildings such as precision machinery, instruments, magnets, chemicals, optics, and food, use multi-story structures. . Multi-story building structures are often hybrid structures and frame structures.
The shape of multi-story buildings is mostly long strips or changes from long strips, such as L-shaped, C-shaped, H-shaped, W-shaped, G-shaped, etc.; this is to meet the lighting and ventilation requirements of the room. Therefore, multi-story building structures can distinguish two main directions: longitudinal and transverse. The physical characteristics of a long house determine that the house has greater longitudinal stiffness and better stability while it has minor transverse stiffness and poorer strength; this issue must always be considered in the specific structural layout.
2. High-rise structure
High-rise structures are increasingly used in cities. Buildings with eight floors and above are generally considered to be high-rise buildings. High-rise buildings have low lateral stiffness and poor stability.
As the height of a house increases, the wind and seismic effects that the structure withstand significantly increase. Therefore, high-rise structures must bear both vertical and large horizontal loads. The thin and tall shape of high-rise buildings is naturally unfavorable for resisting horizontal loads. Thus, fighting lateral forces has become a key and difficult point for high-rise building structures.
In addition to ensuring the strength of the building structures against lateral forces, high-rise structures must also control lateral deformation under the action of lateral forces because excessive lateral deformation will make people feel uncomfortable and because excessive deformation will cause infill walls and Building decoration cracks or falls off because excessive lateral deformation will cause damages in the main structure, increase additional internal forces, and even cause structural collapse. Shear wall structures and frame shear designs have strong lateral force resistance due to shear walls and are often used in general high-rise structures.
3. Super high-rise
High-rise buildings with more than thirty floors are sometimes called supertalls. For super high-rise structures, the lateral force resistance capacity of the frame shear structure sometimes cannot meet the requirements, and the complete shear wall structure affects the use function of the house.
At this time, the cylinder structure can be used. The cylinder evolved from the shear wall because engineering experience and research have found that the ability to resist lateral forces can be significantly improved by enclosing the shear wall into a closed cylinder. The shape of the cylinder may be circular, square, or other shapes.
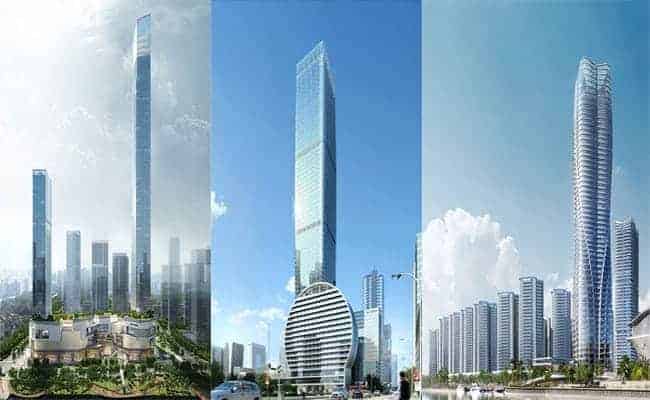

The cylinder can be used alone, such as the cylinder-in-cylinder structure and the bundled cylinder structure; it can also be used with a frame, such as the frame cylinder structure, referred to as the frame cylinder. A frame-tube structure with a single cylinder in the center and a frame around it is called a core tube structure. In structural design, cast-in-place concrete stairwells and elevator shafts are often used as cylinders to improve the structure’s ability to resist lateral forces.
Large span structure
Large span structures are generally single-story. Multi-story large-span building is technically difficult and expensive, and should only be considered when land prices are extremely high. The long-span structures are all public or industrial buildings and are tall. The roof structure of a large-span building structures are a technical difficulty.
There are many types of roof structures, including wooden roof trusses, steel roof trusses, concrete roof trusses, steel grids, steel grid shells, concrete arches, concrete thin shells, concrete folded panels, etc. Roofing materials are often lightweight materials. Single-story structures with small spans are technically very easy and have few applications in modern cities.

Conclusion
There are a wide variety of building structures. In addition to the commonly used ones, there are also folded plate structures, suspension structures, membrane structures, inflatable structures, etc.; these structures have applications but not many and are mainly used in large-scale buildings with more significant stress and complexity and in pursuit of structural design—a novelty in architecture. Within the same type of structural form, there are also many variations. In the same structure, several structures are combined, such as the inner frame, bottom frame, etc.














