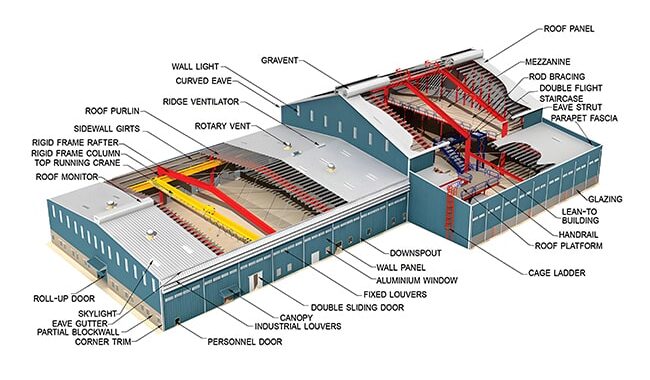
El empalme de estructuras de acero incluye el empalme en el taller y en la obra. Los métodos de empalme…
Introduction: Fire Prevention for Steel Buildings
Steel has reshaped modern architecture, offering unmatched efficiency, load-bearing capacity, and design flexibility. From expansive warehouses to high-rise towers, its advantages are undeniable. Yet, amid its structural strengths lies a critical vulnerability: steel’s performance under heat. Although inherently non-combustible, steel can lose its mechanical strength rapidly when exposed to high temperatures, placing entire buildings at risk of collapse during fire events. As such, fire prevention for steel Buildings is not merely advisable—it is imperative.
The Thermal Weakness of Steel
Unlike timber or combustible materials, steel does not burn. However, its resilience is compromised when heated. Research and real-world incidents confirm that at temperatures between 450°C and 650°C, steel begins to weaken and deform. In severe fire conditions, unprotected steel can lose its load-bearing capacity in as little as 15 minutes. This degradation occurs not through combustion, but through a process of softening that results in structural instability—an outcome with potentially devastating consequences.
To mitigate this, building codes worldwide mandate minimum fire-resistance ratings for steel structures, tailored to their function and occupancy. These standards are not arbitrary; they reflect the urgency of prolonging structural integrity long enough for evacuation and firefighting interventions.

Approaches to Fire Prevention for Steel Buildings: Principles and Practices
Effective fire prevention strategies focus on one goal: slowing the rate at which steel heats up, thereby preserving its structural function during a fire. Several practical solutions have been developed, each with distinct characteristics and appropriate use cases.

Intumescent and Cementitious Coatings
Intumescent coatings are among the most versatile solutions. Applied like paint, these coatings swell upon heating, forming a thick, insulating char layer. This thermal barrier delays heat transfer, often extending fire resistance by 1 to 2 hours, depending on thickness and application. Their lightweight and aesthetic compatibility make them ideal for architectural elements where visual exposure matters.
In contrast, cementitious coatings—composed of mineral-based compounds such as gypsum and vermiculite—operate on a different principle. Rather than expanding, they resist heat via low thermal conductivity. These materials are typically applied in thicker layers and are more suited to mechanical rooms, basements, or industrial spaces where finish quality is secondary to durability.

2. Fireproof Panels and Cladding
Where coatings are impractical or insufficient, fire-resistant boards provide a robust alternative. These pre-formed panels—made from materials such as calcium silicate or perlite—are affixed directly to steel members, offering consistent protection regardless of humidity, substrate conditions, or mechanical stress. Their high resistance to impact and abrasion makes them a practical choice in environments with high traffic or physical wear.
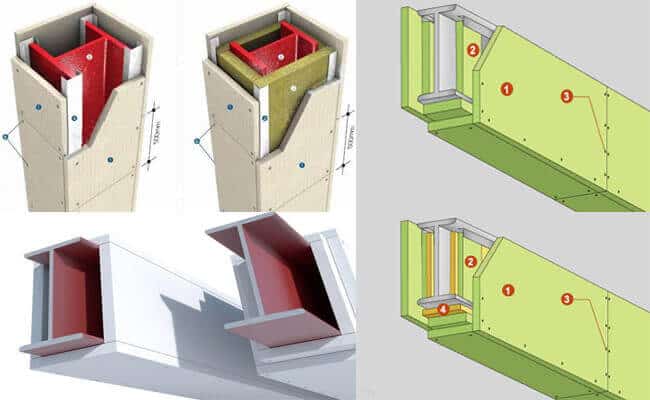
3. Encasement with Concrete or Plaster
Another established method involves encasing steel elements in concrete or plaster, creating a physical separation from flames. Concrete encasement, often reinforced with steel mesh, provides excellent fire resistance while simultaneously increasing a structure’s mechanical robustness. However, the added weight and labor intensity can limit its suitability in projects with strict loading or installation constraints.

4. Water-Filled Members (Water Jackets)
A less conventional yet highly effective strategy involves circulating water inside hollow steel sections. Acting as a built-in cooling system, this “water jacket” concept absorbs and dissipates heat during a fire, keeping the steel below critical temperatures. While technically complex and maintenance-intensive, it offers exceptional protection in high-risk industrial or critical infrastructure applications.
5. Thermal Insulation and Passive Shielding
For interior or non-load-bearing elements, thermal insulation blankets or refractory shielding offer cost-effective fire prevention for steel buildings. These systems function by slowing heat absorption and are particularly useful in mid-rise or residential buildings where full-scale fireproofing may not be feasible. Passive strategies—such as placing structural steel behind fire-rated walls—can also fulfill fire resistance requirements without additional surface treatments.
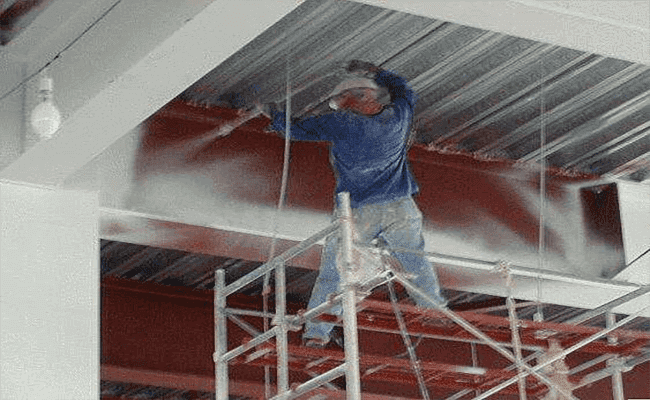

Tailoring the Strategy to Context
Selecting the proper method for fire prevention for steel buildings depends on various interrelated factors:
- Building Use and Risk Profile: Hospitals or high-occupancy structures demand longer fire resistance than agricultural storage facilities.
- Design Complexity: Decorative or geometrically irregular components may benefit more from intumescent coatings than rigid boards.
- Environmental Exposure: High humidity or coastal conditions may limit the durability of certain materials.
- Cost vs. Maintenance: While coatings are often cheaper to install, they may require more frequent inspections than concrete encasement.
Ultimately, fire safety is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Engineers must weigh performance, aesthetics, budget, and regulatory compliance when designing protective systems.
Fireproofing Is Not Forever: Maintenance Matters
No fire protection system is immune to time. Coatings may peel, boards may crack, and environmental wear can undermine long-term performance. Regular inspections—ideally aligned with annual building maintenance cycles—are essential. In most cases, fireproof coatings are paired with anti-corrosion primers, offering dual protection against both flame and rust. Still, manufacturers’ guidelines must be followed, and any signs of degradation should prompt immediate repair or reapplication.
FAQs about fire prevention for steel buildings
Why is fire prevention for steel buildings necessary?
Steel may not burn, but under fire conditions, it weakens quickly. Without protection, this can lead to catastrophic structural failure within minutes.
Which fireproofing method is best?
There’s no universal solution. Intumescent coatings are versatile and aesthetic, while boards and encasements are more robust for industrial applications.
How long can fireproofing extend protection?
Properly applied materials can provide fire prevention for steel buildings for 30 minutes to 3 hours, depending on the system used and the severity of the fire.
Can fireproofing withstand moisture?
Some coatings are sensitive to humidity, but fireproof boards and concrete encasement offer better resilience in wet or coastal environments.
Is dual protection (fire + corrosion) possible?
Yes. Most fireproofing systems include an anti-corrosion primer layer to extend the life of steel components under varied environmental conditions.
Conclusion: Integrating Safety into Steel’s Strength
Steel may offer extraordinary advantages in construction, but without proper fire prevention for steel buildings, its benefits can be undermined in minutes during an emergency. By choosing appropriate fireproofing systems and committing to ongoing maintenance, project teams can ensure that steel buildings remain safe, durable, and compliant with evolving fire codes. Ultimately, fire safety is not a technical afterthought—it is a design responsibility that defines resilience.